Electronic Engineering and Computer Science
- MIT 6.01 EECS I
- MIT 6.02 EECS II
- Logic Gates
- OPCODES
- Assembly Instructions
- Electronic Components
- Basic Circult Design
- ASCII Table
- NEC Infrared Transmission Protocol
- Serial Communication
- Serial Peripheral Interface(SPI)
- Inter-Integrated Circuit(I2C)
- IO MUX & Arbiter
- RTOS
Computer Architecture
- Instruction Set Architecture
- Microarchitecture
- Register_Transfer Level

Electronic Circuit Schematic
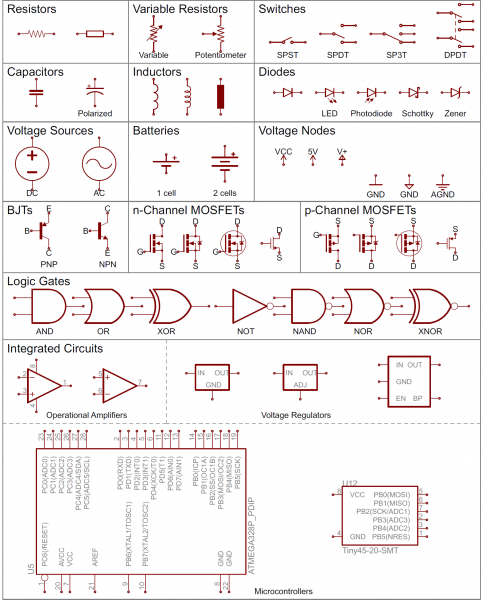
Processor Design
- Analyze the instruction set to determine the requirements for the data path.
- Select appropriate components for the data path.
- Connect the components to establish the data path.
- Analyze the implementation of each instruction to determine the control signals.
- Integrate the control signals to form a complete control logic.
Jargon Glossary
ADCsAnalog-to-Digital ConverterAddressing ModesRegister Addressing/ Memory Direct Addressing/ Indirect Addressing/ Indirect Addressing with Offsets/ Etc.AHBAMBA High-Performance Bus, Fast/High-Bandwidth InterfacesAIRCRApplication and Reset Control Register, Allows for reconfiguration of Data Memory Endianness => 0/Little Endian; 1/Big EndianALUArithmetic Logical UnitAMBAAdvanced Micro-controller Bus ArchitectureAmdahl's lawis a rule of thumb in computer science used to evaluate the potential speedup in a system when improving only a portion of its components. It quantifies the theoretical speedup of a system that can be achieved by enhancing a specific part of it, taking into account the fraction of the task that remains unchanged. It is often used in the context of parallel processing to determine how much a parallel program will speed up due to running on multiple processors. In the field of computer architecture, it helps to understand that even if part of the system is made much faster, the total improvement in performance is limited by the part that is not accelerated.Amdahl’s LawIf F is the sequential portion of a calculation, and (1 – F) is the portion that can be executed concurrently (in parallel), then the maximum speedup that can be achieved by using N processors is 1/(F + ((1 – F)/N)). So, for example, if F = 0, then with N = 4, speedup is linear and equal to 4, but if F = 50%, then speedup is only 1.6 times faster for 4 times as many processors.APBAdvanced Peripheral Bus, Low Bandwidth Bus; Connected to CPU via Bridge to System BusAperiodiclacking a distinguishable frequency or period, having irregular occurrence. Faults and processing exceptions are in real-time systems are aperiodic due to unpredictability of when or how often they might occur.APIApplication Programmable InterfaceARMAdvanced RISC MachineASCIIShort for the American Standard Code for Information Interchange's character encoding scheme, ASCII encodes special characters from our keyboards and converts them to 7-bit binary integers that can be recognized by a number of programs and devicesASICApplication-Specific Integrated CircuitAsynchronousAn event or stimulus that occurs at any point in time rather than at known predictable points in time - e.g. an external interrupt may occur at any time and will immediately change the thread of execution on a CPU.Async-safemeans that a function is reentrant while handling a signal (i.e. can be called from a signal handler).Atomic OperationA non-interruptable CPU instruction - i.e any instruction that can be fetched and completed before the CPU can be interrupted.BandwidthData transfer per unit time—for example, bytes/secondBaud Rate- In short, baud rate is how fast your data is being transmitted and received. 9600 is the standard rate, but other speeds are typical amongst certain devices. Just remember that all the links in your chain of communication have to be "speaking" at the same speed, otherwise data will be misinterpreted on one end or the other.BCDBinary-Coded Decimal, BCD is a method of representing decimal numbers using binary codes, where each decimal digit (0-9) is represented by a 4-bit binary value (0000-1001). In a packed BCD representation, you can fit two decimal digits within a single byte (8 bits). The upper nibble (4 bits) represents the first decimal digit, and the lower nibble (also 4 bits) represents the second decimal digit.BDMBackground Debug Mode, an variant of JTAG that allows data and instructions to be clocked into and out of a 10-pin interface to a processor.BHBottom Half, Software interfacing to I/O device hardware which services interrupts related to the device, provides basic configuration and control, monitors status, and buffers I/O data - the Top Half makes a Bottom Half usable for application software. Note that Linux normally defines the BH and TH opposite of the definition provided here.Big EndianStore MSB(Most Significant Byte) at smallest address, ie: Byte ordering scheme in which bytes of decreasing significance in a data word are stored at increasing addresses in memory.Binary Semaphorea semaphore that has only 2 states: full and empty; a take on an empty binary semaphore will block the calling thread and a take on a full binary semaphore will change the state to empty; a give on an empty binary semaphore will change the state to full and a give on a full semaphore has no effect.bit manipulationchange certain bits of a register (not all contents)BJTbipolar junction transistorBlock Transfertransfer of data (typically contiguous, but may be a scatter/gather list) that includes multiple memory words/bytes on a bus with automatic addressing of each element in the block - rather than addressing and performing a full bus cycle to transfer each word.Block Oriented DriverA software I/O device interface which enables memory blocks to be transferred to an from the I/O device - rather than one memory word at a time.Bound threadshave system-wide contention scope, in other words, these threads contend with other processes on the entire system.BSPBoard Support Package, the boot code and basic I/O interface initialization code needed by an RTOS to boot and cycle on an embedded system board.BSSuninitialized global C program data - because the data is not initialized, this data need not take up space in non-volatile memory, but must be allocated a data segment in working main memory.Bt878Brooktree Video/Audio encoder which can digitize an NTSC inputBurst TransferA bus transaction which involves an initial address cycle followed by many data read/write cycles terminated by the bus master (similar to Block Transfer, but of unlimited length)Byte-Oriented Drivera device interface which provides the ability to read/write single words/bytes to and from the I/O device one at a timeCache Line Evictiona system event where data that is written back to memory, freeing up a cache lineCache Line Invalidationa system event where a cache line is marked, typically with a status bit called “dirty”, which indicates that the cache line must be reloaded from memory before data is read from itCache Line LockingMany caches have control features allowing a program to lock a particular address into a line of cache preventing this line from being replaced when other addresses are loaded (makes most sense for set associative caches rather than direct mapped) - cache line size varies, but is often 16-64 bytesCBCCipher Block Chaining is a cryptography operational modes used to encrypt data with a cipher block algorithm like the AES, DES or Blowfish. CBC uses small piece of data, instead of processing an entire block at a time, other cryptography operational mode are EBC, OFB, CFB. CBC mode is recommended.CISCComplex Instruction Set ComputerCMSISCommon Microcontroller Software Interface Standard is a set of APIs, software components, tools, and workflows that help to simplify software re-use, reduce the learning curve for microcontroller developers, speed-up project build and debug ARMCMOScomplementary metal-oxide-semiconductor, performance better than BJT(Bipologiction transistor) and TTL(transit transistor logic)CODECCoder/decoder, a device that converts analog signals to digital to be read by a computer or transmitted over a network, and converts the digital signals back to analog. Sound cards and video cards use this kind of codec.COM Port (Serial Port)- Each device you connect to your computer will be assigned a specific port number. This helps to identify each device connected. Once a device has a port assigned to it, that port will be used every time that device is plugged into the computer. Your device will show up on your computer as either COM# (if you’re on a Windows machine) or/dev/tty.usbserial-########(if you’re on a Mac/Linux computer), where the #’s are unique numbers or alphabetic characters.Concurrency vs. ParallelismThey are not the same! Parallelism implies simultaneous running of code (which is not possible, in the strict sense, on uniprocessor machines) while concurrency implies that many tasks can run in any order and possibly in parallel.Contention Scopeis how threads compete for system resources (i.e. scheduling).CPIClocks Per Instruction, a measure of CPU efficiency with the ideal that a CPU pipeline should have a CPI of 1.0 or less if the pipeline can retire an instruction every clock - if the pipeline is also superscalar such that multiple instruction pipelines may execute, then this type of microparallelism can theoretically yield a CPI less than 1.0CPU boundWhen an application program is unable to execute any faster due to the clock rate of the CPU and the CPICPU pipelineThe use of micro-parallelism in the CPU core to provide a stage of instruction processing every clock such that once the parallel pipeline is started, an instruction is completed every clock; stages typically include: fetch, decode, execution, and write-back as a minimum. The key to pipelining is that it is possible for the pipeline to fetch, decode, execute, and write back all at the same time for four instructions at various stages; each instruction will actually take multiple cycles to complete, but in the aggregate one instruction is completed every clock (note that pipelines may also be superscalar such that whole pipelines may be run in parallel as well).CSMA/CDCarrier Sense Multi-Access / Collision Detection, a protocol used in ethernet to detect when a node is already transmitting on the shared link and to back off and attempt to use the network later.DACs(Digital-to-Analog Converter)DAPDebug Access PortData, Stop, and Parity Bits- Each packet of data sent to and from the terminal has a specific format. These formats can vary, and the settings of your terminal can be adjusted accordingly to work with different packet configurations. One of the most common configurations you'll see is 8-N-1, which translates to 8 data bits, no parity bit, and one stop bit.Data segmentA memory region reserved for global variables and constants in a C program thread; most often each thread has its own data segment (note that most programs include a Stack, Data, and Text segment as a minimum).DDIDevice Driver InterfaceDDRDouble data rate; a bus data encoding technique where read or write data is transferred on both edges of a reference clock rather than just one (rising edge and falling edge); this doubles the data rateDMADirect Memory Access, a hardware state machine independent of the CPU core which is able to transfer data in or out of memory without directly executing core instructions, thus allowing the core to continue execution while regions of memory are copied, updated by an I/O device, or read out to an I/O deviceDouble-bufferingA technique often used in continuous media applications to allow for data acquisition into one buffer while another is being read out and processed; when the acquisition buffer is full, the buffer pointers are swapped such that the newly acquired data is processed and the already processed buffer can now be used for acquisition.DoublewordA 64-bit data item. The contents are taken as being an unsigned integer unless otherwise stated.DSPDigital Signal ProcessorDynamic linkingA technique where PIC software compiled into an object file format, such as ELF, can be loaded and linked into existing software on an RTOS platform on the fly after the RTOS has already been booted and is up and running.EABIEmbedded Application Binary Interface: Provides details on how a binary must be compiled and interfaced with platform componentsEEPROMelectrically erasable programmable read-only memory, means a user-modifieable ROM. It can be erased and reprogrammed (written to) repeatedly by applying an electrical voltage that is higher than normal.EFSMExtended Finite State Machine, a formal method based upon state machines which extends the basic state transition on I/O to include side effects on transitions such as global data update and data processing.ELFExecutable and Linking Format, an object file format which includes significant annotation and is PIC such that these files can be dynamically loaded and linked and such that they can serve for supporting debug and trace analysis to map addresses back to source codeEMPUEmbedded Micro Processor UnitEndiannessByte ordering. The scheme that determines the order that successive bytes of a data word are stored in memory. An aspect of the system’s memory mapping.Event-based profilingA profiling technique where the PC is saved into a trace buffer whenever events of a specific type exceed a threshold—for example, when data cache misses exceed N misses, the PC is saved into a trace bufferFCFSFirst come, first served; the policy often used by an RTOS when services/threads are at the same priority level—that is, the first service ready is the first one dispatchedFGTsfloating gate transistors, are complementary MOS-based bit cells. When there is no charge on the floating gate, a pulse on the control gate causes current to flow. At this point, the transistor acts normallyFIFOFirst in, first out; a policy for queues (e.g., a dispatch queue) where the first element queued is always the first element de-queuedFPGAField Programmable Gate Array, an array of generic transistors which can be programmed once or on power-up to provide combinational logic and state machines for digital processingGFCIGround Fault Circuit Interrupter (North American Style)GPIOGeneral Purpose Input OutputHALHardware Abstraction Layer, standardized definitions for the SysTick, NVIC, System Control Block registers, MPU registers, FPU registers, and core access functions.HalfwordA 16-bit data itemHamming codeA bit encoding used to detect and correct SBEs (single bit errors) and to detect MBEs (multi-bit errors) for memory devices that may be subject to SEUs.Harvard architectureA core CPU architecture that splits the memory hierarchy into separate instruction and data streams, typically including an L1 instruction cache that is independent of an L1 data cache.HDLHardware Description LanguageHeapA memory space used for dynamic buffer management and/or dynamic allocation of memory as requested by an application; heap space is memory outside the data, text, and stack segments and is most often reserved by the boot or RTOS during initialization.hFE(hybrid parameter forward current gain common emitter)(to measure the transister)HSTLHigh-speed transceiver logic; a 0.0-1.5v logic level standard used for high-speed single-ended digital IO, most often for memory IO (speeds of 180 MhZ and greater).HWICHardware in circuit; a concept whereby debug and trace tools have hardware probes in circuit with a CPU by interfacing to signals coming from the CPU/SoC ASIC to the rest of the system board for the purpose of snoop tracing and/or control—for example, JTAG debug emulator, Vision ICE Event Trace, RISCWatch trace port probe, and CodeTEST Universal trace probe.I²CThe Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C) Protocol is a protocol intended to allow multiple "peripheral" digital integrated circuits ("chips") to communicate with one or more "controller" chips. Like the Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI), it is only intended for short distance communications within a single device.ICEIn-circuit emulator; a debug and trace device that monitors all IO pins on a CPU/SoC ASIC, provides memory trace, external interrupt trace, JTAG, and IO pin trace, and emulates the state of the system, including all registers, cache, and addressing, to aid in firmware development and board verificationIMUInertial Measurement Unit, for orientation sensorsInterrupt handlerDuring the normal CPU pipeline processing (fetch, decode, execute, write-back) an external device may assert an signal input or an internal sub-block may also assert a signal input to the CPU core that causes it to asynchronously branch to an interrupt vector (a memory location) where basic code called the handler acknowledges and services the hardware and then calls application ISRsInterrupt latencyThe delay between assertion of an interrupt signal by a device and the time at which the PC is vectored to an interrupt handler is known as the interrupt latency.Interrupt vectorAn address in memory where the CPU sets the PC after an interrupt signal is asserted, causing the CPU to asynchronously branch to this location and to execute the instruction there; normally a CPU will have a number of interrupt inputs (e.g., x86 IRQ0-15), and each signal asserted causes the CPU to vector to a different address such that different handlers can be associated with each interrupt signal.IO MUXInput/Output Multiplexer 是一种电路设计技术,用于在多个输入或输出信号之间进行选择和切换。它允许一个引脚或一组引脚在不同的功能之间动态切换,从而节省硬件资源并提高系统的灵活性。IPCInter-Process CommunicationI²S(Integrated Interchip Sound)ISAInstruction Set AlgorithmISA Legacy InterruptIndustry Standard Architecture Legacy Interrupt, specifically refers to x86 architecture IRQ0-15 which have been part of the x86 architecture from the beginning (8086) and support a number of well-known PC devices and services such as booting from a hard drive.Isochronaluniform in time, having equal duration, recurring at regular intervalsISRInterrupt Service Routine, the application level of an interrupt handler which is often a call-back function registered with an RTOS that installs the interrupt handler at an interrupt vector.JTAGJoint Test Action Group, an IEEE committee that standardized the concept of boundary scan and the TAP (test access port), which is used to verify integration of ASICS in a system (boundary scan), but is now also typically used in firmware development to control and single-step a CPU by loading data and commands through the TAP with JTAG. JTAG includes the following signals: TDI (Test Data In), TDO (Test Data Out), TRST (Test Reset), Clock, and Test Mode Set.Keep-aliveAn indication from a thread/process/task on a system that it is functioning normally or perhaps similar indication from a subsystem in a larger system; the keep-alive is most often a simple ID and count indicating that the subsystem/thread/process/task is advancing through its service loop, often referred to as a heartbeat as well.KNNk-Nearest NeighborsLaxityLaxity = (Time_to_Deadline – Time_to_Completion), but the time to the completion of a service can be difficult to determine, so most often an estimate of the Time_to_Completion is used, which is derived from (WCET – Computation_Time_So_far).LCMLeast Common Multiple, the LCM is the smallest number which is also multiple of 2 different numbers - e.g. given x=3, y=5, the LCM(x,y)=15Linking (dynamic or static)Linking is the process by which an executable image is assigned addresses for all function entry points, all global variables, and all constants that may be referenced by other software modules; these addresses can be statically assigned once and for all at a pre-determined offset in physical memory (static linking) or may be position-independent such that only relative addresses are assigned until the module is loaded, at which time physical addresses are derived from the relative (dynamic linking).Little EndianStore LSB(Least Significant Byte) at smallest addressLLFLeast Laxity First, a dynamic priority policy where services on the ready queue are assigned higher priority if their laxity is the least (where laxity is the time difference between their deadline and remaining computation time) - this requires the scheduler to know all outstanding service request times, their deadlines, the current time, remaining computation time for all services, and to re-assign priorities to all services on every preemption. Estimating remaining computation time for each service can be difficult and typically requires a worst-case approximation.Local Echo- Local echo is a setting that can be changed in either the serial terminal or the device to which you are talking, and sometimes both. This setting simply tells the terminal to print everything you typeLTTLinux Trace Toolkit, a tool that traces events in the Linux kernel, encodes them, and stores a trace of event codes in memory. The event trace can be loaded later into a tool for timing analysisMCSMicro computer SetMCUMicro Controller UnitMIPSMicroprocessor without Interlocked Pipelined StagesMIPSMillions of Instructions Per SecondMMUMemory Management Unit, a block in most CPU cores which provides virtual to physical address mapping, address range checking, and can protect read-only address ranges from unintentional updateMOSmetal-oxide-silicon (MOS) transistorMOSFETmetal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistorMutex Semaphorea specialized semaphore (compared to a binary semaphore) which is specifically used to protect critical sections of code for multi-thread safety - this semaphore is used to guarantee mutually exclusive access to a shared resource such that only one thread may access a common resource at a time - with shared memory this prevents data corruption that could be caused by multiple readers/writers - e.g. if a writer has partially updated a shared data structure, is preempted/interrupted, and then a reader accessed the partially updated data, the data may be completely inconsistentNand Flasha flash memory device which is normally erased to all F’s and writes are bit-wise masked in with an and operationNCVno contact voltageNor Flasha flash memory device which is normally erased to all 0’s and writes are bit-wise masked in with an or operation.NPTLNative POSIX Threads Library, is the GNU C library POSIX. threads implementation that is used on modern Linux systems. NPTL and signalsNUMANon-Uniform Memory Access, Each CPU has local and non-local memory with different access latenciesNVRAMNon-Volatile Random Access Memory, memory which persistently holds data whether or not a system is powered or not - e.g. a battery backed-up DRAM, a Flash memory device, EEPROM, or EPROM.NVSNon volatile memoryObject Codemachine code annotated with symbol information (variable and function names and addresses) and information to support debugging (source file names and locations).OCTCopen circuit time constantOptical navigationUsing computer vision images of a scene to determine ranges to targets and to plan paths to navigate to a target using only video dataPCBPrinted circuit boardPCIPeripheral Component Interconnect, a standard defined by the PCI Special Interest Group to provide CPU, memory, and IO device interconnection for data transportPCI Bus ProbingA process that allows a BIOS or OS software to find all PCI devices and functions on a given PCI bus using configuration space registers.PID ControllerProportional-Integral-Derivative Controller, a controller that sets outputs proportional to error, integrates sensor inputs to find for example velocity from acceleration, and also uses derivatives such as velocity from position measurements in order to control a system and obtain a target operational state - e.g. a cruise control provides acceleration proportional to the difference between current and target speed and integrates to determine when the target will be achieved and when to decelerate.Pollingwhen status is checked periodically (synchronously) by a looping construct.POSIXPortable Operating Systems Interface, a standard for operating system mechanisms and APIs. POSIX includes a number of sub-standards such as 1003.1b which covers basic real-time mechanisms.PPBPrivate Peripherals Bus, Internal PPB - SCB(System Control Block)/NVIC(Nested vector interrupt controller)/MPU(Memory Protection Unit); External PPB - External DebuggingPreemptionwhen the current thread executing on a CPU is placed back on the ready queue by the scheduler and state information saved so that a different thread can be allocated the CPU.Processinstance of a computer program; A thread of execution with stack, register state, and PC state along with significant additional software state, such as copies of all IO descriptors (much more than a task TCB for example), including a protected memory data segment (protected from writes by other processes)PSRProgram Status RegisterPure Functiona function coded so that it only uses stack (no global data at al), depends only in input parameters, and calls only other pure functions is a pure function and is also thread safe.PVCPolyvinyl chloridePWMPulse Width Modulation, a technique to control a motor or other normally analog device by creating a pulse train of digital TTL output to simulate an analog output..QoSQuality of Service, definition of service levels based upon guarantees of resource availability for each service - e.g. processor capacity can be reserved for each service in advance (say 10%) and the system guarantees that this capacity will be available within in a worst case period of time, however may not guarantee all services will meet their deadlines.Rate montonic policy: a priority seheduling policy, the more frequent a service runs, the higher priority it gains. Which means, a task which has shortest service period has top priority, this is to ensure a task responses fastRCCReset and clock controlRCD(Residual Current Device)(European Style)Receive (RX)Also known as Data In or RXI. The RX line on any device is there to receive data. This should be hooked up to the TX line of the device with which you would like to communicate.Reentrantcode means that a program can have more than one thread executing concurrently.Ring Buffera data structure which provides multiple serially reusable buffers - most often used to buffer incoming data from a device interface before it can be processed - likewise for output data before it can be transmitted.RISCReduced Instruction Set ComputerRMRate Montonic, the basic theory formulated by Liu and Layland for fixed priority multiplexing of a single CPU that is intended to provide multiple services over time.RMARate Monotonic Analysis,the process of analyzing the C, T, and D characteristics of a set of services to be executed on a CPU and determination of priorities according to RM policy and feasibility according to a sufficient or better yet, necessary and sufficient test.RMIIReduced Media-Independent InterfaceRound Robina best effort scheme with preemptive time-slicing where the scheduler assigns threads a slice in a fair fashion where all ready threads are given a slice of CPU and put back on the end of the queue if neededRPCRemote Procedure CallRTOSReal Time Operation System, a scheduling and resource management framework for implementation of software services that must provide responses to requests prior to well defined deadlines.RTCPReal-Time Control ProtocolRTPReal-Time Transport ProtocolSemaphorean RTOS mechanism which can be used for synchronization of otherwise asynchronous tasks in order to coordinate resource usage such as shared memory, or to simply indicate a condition such as data is available on an interface.SEUSingle Event Upset, a phenomena where a memory bit is flipped due to an environmental influence such as electromagnetic radiation. The bit’s original value may be restored if the SEU can be detected and corrected by a system monitoring technique.SDLSpecification and Description LanguageSDRAMSynchronous Dynamic Random Access MemoryShared Interruptwhen an interrupt can be asserted by multiple devices, it is shared and requires the interrupt handler to poll status - I.e. the handler must read the status of every device that may have asserted the interrupt to figure out which device in fact did.SMDSurface Mount DeviceSMPSymmetric MultiprocessingSOAService-Oriented ArchitectureSoCSystem On-a-Chip, an ASIC which includes one or more CPU cores, a bus, and I/O interfaces such that it essentially places devices previously on a board in earlier products on a single ASICSPISerial Peripheral Interface is an interface bus commonly used to send data between microcontrollers and small peripherals such as shift registers, sensors, and SD cards. It uses separate clock and data lines, along with a select line to choose the device you wish to talk to.SPPSerial Port Profile, is a Bluetooth profile that allows for serial communication between a Bluetooth device and a host/slave device. With this profile enabled, you can connect to a Bluetooth module through a serial terminal.SRAMStatic Random-Access MemorySR-LatchSet & Reset LatchStack Segmenta segment of memory allocated for a thread which provides buffer space for function arguments and local variables - each application thread, the kernel thread, ISRs, and signal handlers typically all have their own stack space for the purpose of parameter passing and local variable instantiation.SWDSerial Wire DebugSWICSoftware In Circuit, a technique where software instrumentation is used to trace execution, e.g. logging messages to a file from an application.Taskset of program instructions loaded in memoryTEthermal equilibriumTCBTask Control Block, the data structure associated with a VxWorks task which contains all task data in addition to task stack and context.TFTPTrivial File Transfer Protocol, a simplified FTP (File Transfer Protocol) which allows a client to download files from one known directory in a file system.- Thread is a sequence of such instructions within a program that can be executed independently of other code. unit of CPU unilization with its own program counter and stack.
Thread Safecode is thread safe only if it functions as expected when executed simultaneously by multiple threads. A function that is designed to be reentrant or a pure function is thread safe.TTLTransistor to Transistor Logic, traditional 5v digital logic levels.TTLTime-To-Live, A counter in a datagram that is decremented on each node-to-node hop such that the packet is discarded when TTL=0; this prevents a packet from hopping around the network indefinitely and creating a problemTTYeletypewriter or teletype. Much like terminal is synonymous with the terminals of old, so too is teletype. These were the electromechanical typewriters used to enter information to the terminal and, thus, to the mainframe. When working with terminals on Mac and Linux, you will often see tty used to represent a communication port rather than 'COM port'.Transmit (TX)- Also known as Data Out or TXO. The TX line on any device is there to transmit data. This should be hooked up to the RX line of the device with which you would like to communicate.UARTUniversal Asynchronous Receiver / TransmitterVoIPVoice over IP, a protocol for transporting voice duplex audio over the Internet protocol.Von Neumann architectureis a digital computer architecture based on the concept of stored program computers, where both program data and instruction data are stored in the same memory. This architecture was designed by John Von Neumann in 1945 vs Harvard architecureWatchdog Timera hardware based interval timer which counts down (or up) and when it reaches zero (or all F’s) it generates an H-reset signal causing the system to re-boot - critical software services are expected to post keep-alives to a system sanity monitor which normally in turn resets the watchdog timer before it expires. If the software loses sanity, I.e. the sanity monitor fails to reset the watchdog timer (e.g. if a deadlock were to occur), then the idea is that the system will be able to recover by re-booting.WordA 32-bit data itemWord SizeThe operand size of the Instruction Set Architecture (ISA)Yieldwhen a thread of execution gives up the CPU resource voluntarily through a system API call – e.g. in VxWorks pause(). Yields may include transition from executing to pending, delayed, or suspended states. Note: In a priority preemption, a thread will transition from executing to ready.
environments
unit quantites
| suffix | multiplier |
|---|---|
| T | 1012 |
| G | 109 |
| M | 106 |
| k | 103 |
| m | 10-3 |
| u | 10-6 |
| n | 10-9 |
| p | 10-12 |
| f | 10-15 |
HOMEWORKS_I
- [x]basic types
- [x]numeric expressions
- [x]relations boolean
- [x]mixed types
- [x]variable binding
- [x]fun with functions
- [x]functions and scope
- [x]scoping
- [x]square
- [x]fourth power
- [x]odd test
- [x]from point a to point b
- [x]evaluate a quadratic at a point
- [x]distance from point to line
- [x]if statements
- [x]compare
- [x]arithmetic if
- [x]clipping shears
- [x]clip clop
- [x]multiple times
- [x]multiple times, again
- [x]a la mod
- [x]muad-div
- [x]primo
- [x]powers of 2
- [x]perfectly square
Page Source