Electronic Components
Cable standards
Comparison of SWG (red), AWG (blue) & IEC 60228 (black)
The 10 Percent Rule:
This rule is a standard method for selecting R1 and R2 that takes into account the load and minimizes unnecessary power losses in the divider.
LED (Light Emittin Diode)

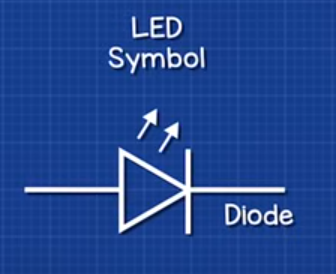
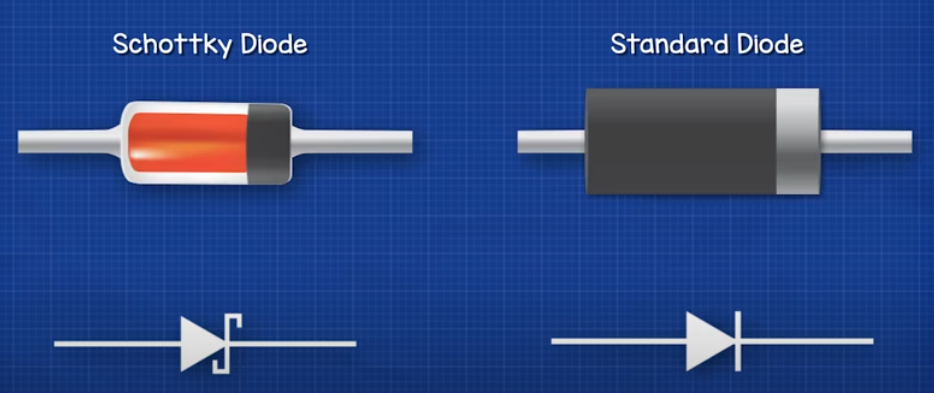
Diode
- Standard diode
- Schottky diode
N-Type
the intrinsic elemental semiconductors, such as silicon and germanium, there are hybrid compounds—compounds such as gallium arsenide. Other semiconductors are made by introducing impurities into a silicon lattice. For example, an atom in the chemical group of phosphorous, arsenic, and antimony can replace one of the silicon atoms in a lattice without affecting the lattice itself too much. However, each of these impurities has one more electron in its valence level than the silicon atom has; this extra electron, for which there is no room in the valence band, takes a place in the conduction band and can conduct electricity. A semiconductor with impurities of this sort is called an n- type semiconductor, and the extra electrons are called donor electrons
P-Type
Atoms of elements in the same chemical group as boron, aluminum, and gallium have one less valence electron than silicon has. If an atom is added to a lattice of silicon as an impurity, there is one less electron than is needed to form a bond that holds the lattice together. This electron must be provided by the electrons of the valence band of the lattice material, and holes are created in this band. These holes act as positive charge carriers. The impurity atoms are called acceptors. A semiconductor with such impurities is called a p- type semiconductor.
Resistor
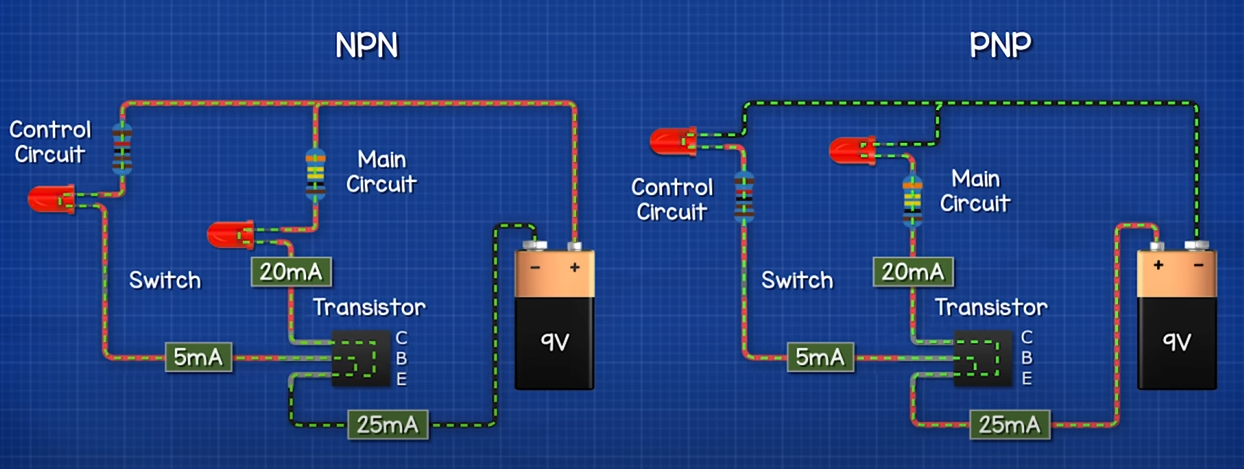
Transistor
Transistors are small electronic components with two main functions: 1. Switches circuits on and off 2. Amplify singals
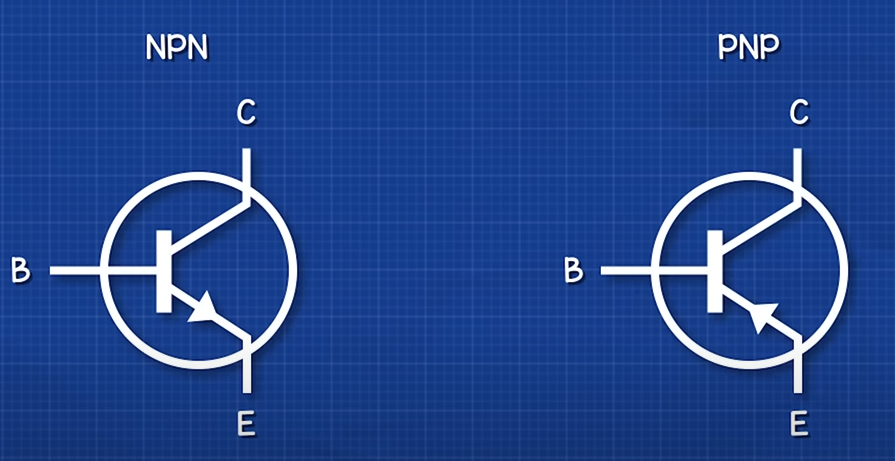
- 3 Pin(Emitter, Base, Collector), typically 0.6-0.7v, ~1mA to base pin
- Current gain (β) = Collector current / Base current
- Current control the Base Pin
- Bipolar & Field Effect
- BJT(Bipolar Junction Transistors)
Inductor
Capacitor
A capacitor stores electric charge. It’s a little bit like a battery except it stores energy in a different way. It can’t store as much energy, although it can charge and release its energy much faster. This is very useful and that’s why you’ll find capacitors used in almost every circuit board.
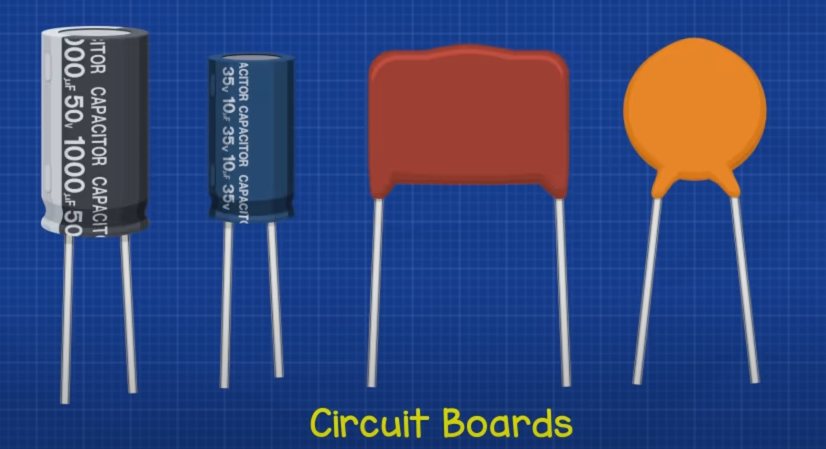
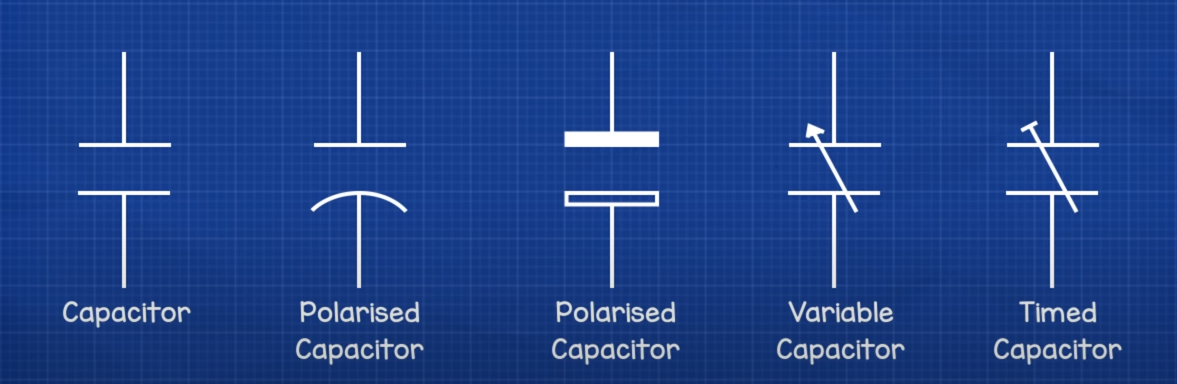
Voltagethe maximum voltage the capaciator can handleCapacitancein units of Farads- in large buildings is for power factor correction
- smooth out peaks when converting AC to DC
- smooth the power supply out to look more like DC
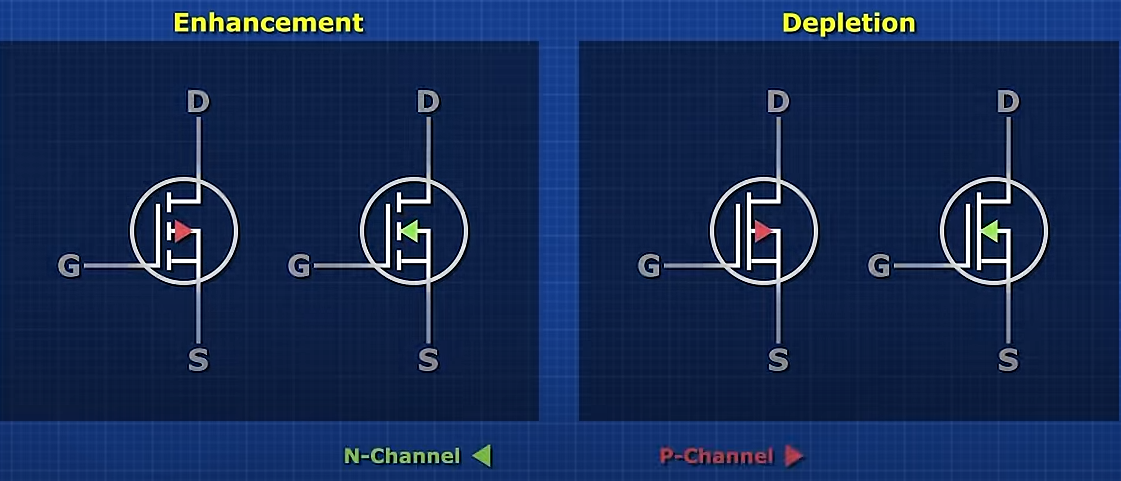
MOSFET
3 Pins: Gate, Drain, Source
- Varying the voltage provided to Gate Pin, Main circuit from Pin Drain to Pin Source will be effected
- Voltage Control the Gate Pin, more energy efficient in contrast to a transistor
- Enhancement Type (Normally OFF), Depletion Type (Normally ON)
Potentiometer
Optocoupler
Optocouplers are integrated electronic components