rtos
RTOS (Real Time Operation System)
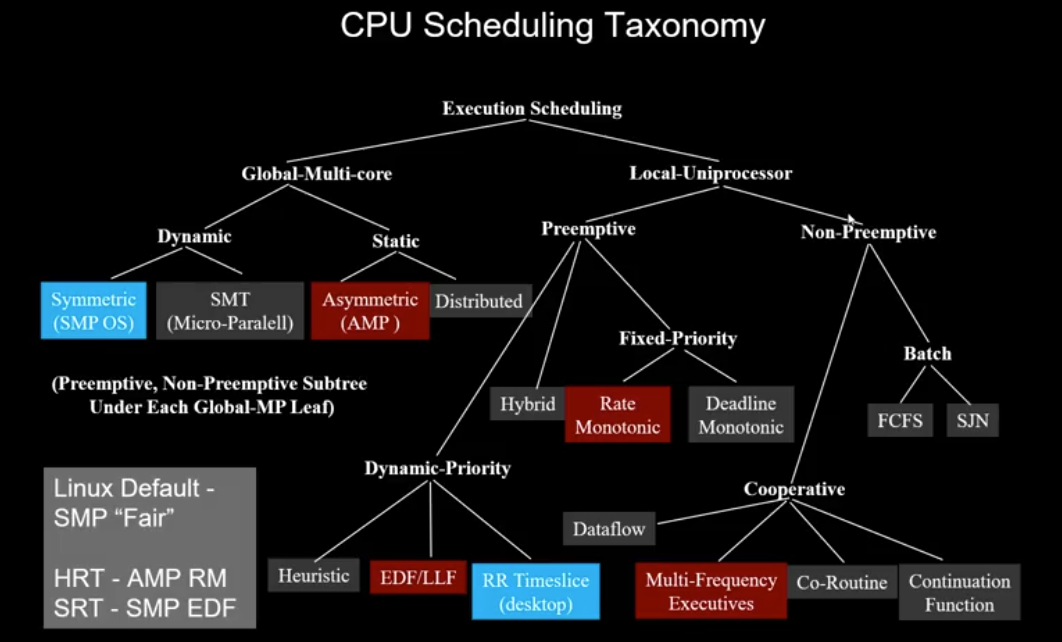
- CFS Complete Fair Scheduler
- AMP Asymmetric Multi-Processing
- SMP Symmertric Multi-Processing
- NUMA Non-uniform memory access
- SMT Simultaneous Multi-threading
- Flynn's Taxonomy {Single Instruction, Multi-instruction} x {Single data, Multi-data}
- RM LUB Rate Monotonic Least Upper Bound
- EDF Earliest Deadline First
Thread Design Pattern
- Thread Pool (Boss/Worker) One thread dispatches other threads to do useful work which are usually part of a worker thread pool. This thread pool is usually pre-allocated before the boss (or master) begins dispatching threads to work. Although threads are lightweight, they still incur overhead when they are created.
- Peer (Workcrew) The peer model is similar to the boss/worker model except once the worker pool has been created, the boss becomes the another thread in the thread pool, and is thus, a peer to the other threads.
- Pipeline Similar to how pipelining works in a processor, each thread is part of a long chain in a processing factory. Each thread works on data processed by the previous thread and hands it off to the next thread. You must be careful to equally distribute work and take extra steps to ensure non-blocking behavior in this thread model or you could experience pipeline "stalls."
Task vs Process
Task
A thread with normal thread state including stack, registers, PC, but also including signal handlers, task variables, task ID and name, priority, entry point, and a number of state and inter-task communication data contained in a TCB(Task Control Block) for VxWorks RTOS or Linux kernal descriptor.
- Only exists in Linux kernel space
- For an RTOS, this is the main execution context is kernal space (no user space)
- Tasks can not be created, controlled or accessed in Linux user space
- Tasks can implement a Linux process or threads within a process
- Kernel modules can create kernel tasks
- Kernel tasks will be created for a user space process and threads it contains as needed for Linux Process and NPTL excution model
Process
A process contains 1 or more threads in a protected address space, A process is a thread of execution with stack, register state, and PC state along with significant additional software state such as copies of all I/O descriptors (much more than an RTOS task + TCB) including a protected memory data segment (protected from writes by other processes)
- Only exists in Linux user space
- Process main thread is mapped onto a Linux kernel task
- Serves as a container for 1 or more threads in a common address space
- Protected address space (wild write in another process can not impact)
- Additoinal POSIX threads created are mapped via NPTL onto Linux kernel tasks
- The Process is an old model for execution in Linux for multi-programming
- Very safe, isolates and insulates the OS from bad user code and prevents one applicatoin form destabilizing another when user code is buggy
Threads
- Race Condition is the ability of two or more threads to execute in overlapping time periods
- Thread-per-connection assigns one unit of work to one thread for the duration of the unit of work's execution
- Event-driven-Threading uses asynchronous I/O request, callbacks and multiplexed I/O with a loop which handles a callback off to a waiting thread.
- A process is an OS Abstraction representing binaries in action
- A Binary is a Dormant programs residing on a storage medium and ready to execute.
- Race conditions are avoided by making critical regions atomic.
- Parallelism is not possible on a platform which only has a single processor or execution unit.
- An application which uses event driven threading will typically not see a performance improvement by increasing the number of threads to a value higher than the number of processors available in hardware.
- State machines are in many cases a design pattern which can be used as an alternative to threads.
Linux User space vs Kernel space
Linux has 2 address spaces - user and kernel
Kernel space directly interfaces to hardware and manages all resources
- Provides protected address spaces for user processes(that can have threads mapped onto kernel tasks)
- Provides security and stability
- Driver and kernel modules have different development, debug, and test strategies!
User space protects the system from errors and provides security & stability
- All applications interfacing to hardware must go through a driver and/or system call
- All applications run in within a protected address and resource domain
can we have both? - with care
- Sub-millisecond time critical, direct hardware interfaces must be in a driver kernel module
- Millisecond or less predictable response (soft RT and BE) services can operate in user space
- Carefully configure a Linux platform (real-time distro) and allocate services to both user space and kernel space based on requirements and timing constraints(carefully!)
RTOS/NPTL provides common scheduling frames for:
- Fixed priority preemptive
- Rate Monotonic
- Deadline Monotonic
- Dynamic priority preemptive
- EDF
- LLF
- Non-preemptive cooperative
- Multi-Frequency executive
- dataflow
Rate Monotonic theory - optimal priority policy
Example
#define _GNU_SOURCE
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sched.h>
#define NUM_THREADS 64
#define NUM_CPUS 8
typedef struct
{
int threadIdx;
} threadParams_t;
pthread_t threads[NUM_THREADS];
pthread_t mainthread;
pthread_t startthread;
threadParams_t threadParams[NUM_THREADS];
pthread_attr_t fifo_sched_attr;
pthread_attr_t orig_sched_attr;
struct sched_param fifo_param;
#define SCHED_POLICY SCHED_FIFO
#define MAX_ITERATIONS (1000000)
void print_scheduler(void)
{
int schedType = sched_getscheduler(getpid());
switch(schedType)
{
case SCHED_FIFO:
printf("Pthread policy is SCHED_FIFO\n");
break;
case SCHED_OTHER:
printf("Pthread policy is SCHED_OTHER\n");
break;
case SCHED_RR:
printf("Pthread policy is SCHED_RR\n");
break;
default:
printf("Pthread policy is UNKNOWN\n");
}
}
void set_scheduler(void)
{
int max_prio, scope, rc, cpuidx;
cpu_set_t cpuset;
printf("INITIAL "); print_scheduler();
pthread_attr_init(&fifo_sched_attr);
pthread_attr_setinheritsched(&fifo_sched_attr, PTHREAD_EXPLICIT_SCHED);
pthread_attr_setschedpolicy(&fifo_sched_attr, SCHED_POLICY);
CPU_ZERO(&cpuset);
cpuidx=(3);
CPU_SET(cpuidx, &cpuset);
pthread_attr_setaffinity_np(&fifo_sched_attr, sizeof(cpu_set_t), &cpuset);
max_prio=sched_get_priority_max(SCHED_POLICY);
fifo_param.sched_priority=max_prio;
if((rc=sched_setscheduler(getpid(), SCHED_POLICY, &fifo_param)) < 0)
perror("sched_setscheduler");
pthread_attr_setschedparam(&fifo_sched_attr, &fifo_param);
printf("ADJUSTED "); print_scheduler();
}
void *counterThread(void *threadp)
{
int sum=0, i, rc, iterations;
threadParams_t *threadParams = (threadParams_t *)threadp;
pthread_t mythread;
double start=0.0, stop=0.0;
struct timeval startTime, stopTime;
gettimeofday(&startTime, 0);
start = ((startTime.tv_sec * 1000000.0) + startTime.tv_usec)/1000000.0;
for(iterations=0; iterations < MAX_ITERATIONS; iterations++)
{
sum=0;
for(i=1; i < (threadParams->threadIdx)+1; i++)
sum=sum+i;
}
gettimeofday(&stopTime, 0);
stop = ((stopTime.tv_sec * 1000000.0) + stopTime.tv_usec)/1000000.0;
printf("\nThread idx=%d, sum[0...%d]=%d, running on CPU=%d, start=%lf, stop=%lf",
threadParams->threadIdx,
threadParams->threadIdx, sum, sched_getcpu(),
start, stop);
}
void *starterThread(void *threadp)
{
int i, rc;
printf("starter thread running on CPU=%d\n", sched_getcpu());
for(i=0; i < NUM_THREADS; i++)
{
threadParams[i].threadIdx=i;
pthread_create(&threads[i], // pointer to thread descriptor
&fifo_sched_attr, // use FIFO RT max priority attributes
counterThread, // thread function entry point
(void *)&(threadParams[i]) // parameters to pass in
);
}
for(i=0;i<NUM_THREADS;i++)
pthread_join(threads[i], NULL);
}
int main (int argc, char *argv[])
{
int rc;
int i, j;
cpu_set_t cpuset;
set_scheduler();
CPU_ZERO(&cpuset);
// get affinity set for main thread
mainthread = pthread_self();
// Check the affinity mask assigned to the thread
rc = pthread_getaffinity_np(mainthread, sizeof(cpu_set_t), &cpuset);
if (rc != 0)
perror("pthread_getaffinity_np");
else
{
printf("main thread running on CPU=%d, CPUs =", sched_getcpu());
for (j = 0; j < CPU_SETSIZE; j++)
if (CPU_ISSET(j, &cpuset))
printf(" %d", j);
printf("\n");
}
pthread_create(&startthread, // pointer to thread descriptor
&fifo_sched_attr, // use FIFO RT max priority attributes
starterThread, // thread function entry point
(void *)0 // parameters to pass in
);
pthread_join(startthread, NULL);
printf("\nTEST COMPLETE\n");
}
Page Source