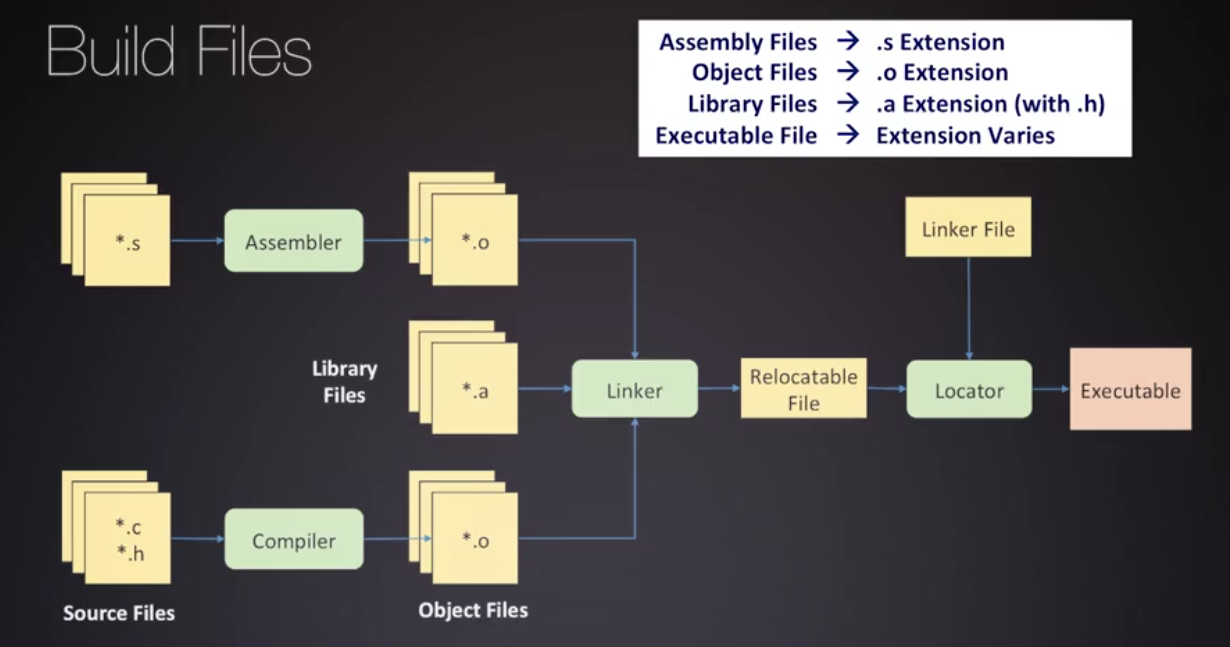
C basic
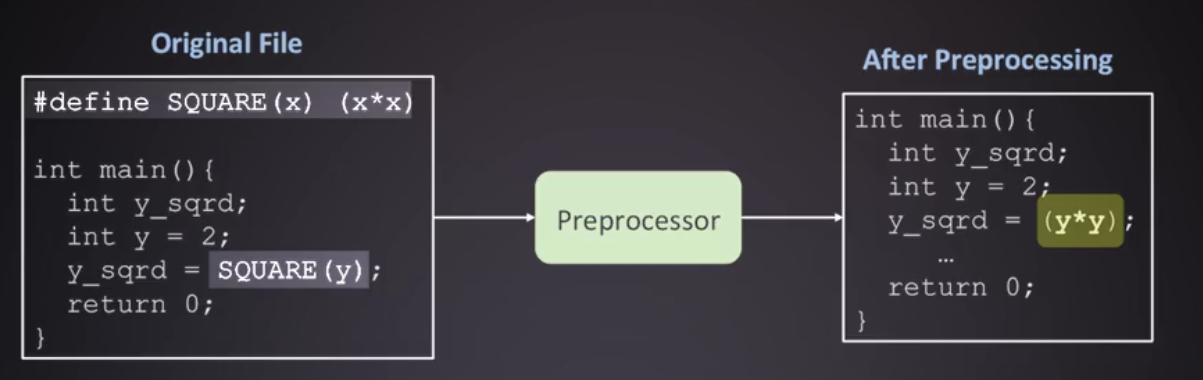
Data types
basic type
| size | type | format specifier |
|---|---|---|
| 1 byte | char |
%c |
| 2 bytes | short |
%d |
| 2 or 4 bytes | int |
%d or %i |
| 4 or 8 bytes | long |
%ld |
| 4 bytes | float |
%f 6-7 precision |
| 8 bytes | double |
%lf 15-16 precision |
#include <stdbool.h>
bool isProgrammingFun = true;
printf("%d", isProgrammingFun); // Returns 1 (true)
// Arrays
int myNumbers[] = {25, 50, 75, 100};
int matrix[2][3] = { {1, 4, 2}, {3, 6, 8} };
char greetings[] = "Hello World!";
printf("%s", greetings);
d_type (man readdir)
/* Standard file descriptors. */
#define STDIN_FILENO 0 /* Standard input. */
#define STDOUT_FILENO 1 /* Standard output. */
#define STDERR_FILENO 2 /* Standard error output. */
struct dirent {
ino_t d_ino; /* Inode number */
off_t d_off; /* Not an offset; see below */
unsigned short d_reclen; /* Length of this record */
unsigned char d_type; /* Type of file; not supported by all filesystem types */
char d_name[256]; /* Null-terminated filename */
};
- DT_BLK This is a block device.
- DT_CHR This is a character device.
- DT_DIR This is a directory.
- DT_FIFO This is a named pipe (FIFO).
- DT_LNK This is a symbolic link.
- DT_REG This is a regular file.
- DT_SOCK This is a UNIX domain socket.
- DT_UNKNOWN The file type could not be determined.
IEEE 754 floating point format
- representing and manipulating floating point quantities
- followed by all the modern computer systems and Microcontrollers
Float VS Double
Float
- Float is for 32-bit representation
- Single precision
%fformat specifier for the float type variable%eformat specifier for float scientific notation
Double
- Double is for 64-bit representation
- Double precision
%lfformat specifier for the double type variable%leformat specifier for double scientific notation
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
float fnum = 78.55674545678;
double dnum = 78.5567676767676;
printf("Number is = %0.9f\n", fnum);
// Number is 78.556747437
printf("Number is = %0.14lf\n", dnum);
// Number is 78.55676767676761
return 0;
}
Enumerations
Enums are an enumerated type builed into C-programming: Integer data type
enum
- Enumeration definition does not reserve memory, only the declaration of an enumerated type
- Multiple implementations exist(per eABI), normally:
unsigned intorsigned int, alternatively: smallest integer type to fit all enumerated values
enum month {
JAUNARY = 1,
FEBRUARY = 2,
MARCH = 3,
APRIL = 4,
MAY = 5,
JUNE = 6,
JULY = 7,
AUGUST = 8,
SEPTEMBER = 9,
OCTOBER = 10,
NOVEMBER = 11,
DECEMBER = 12
};
enum month m = APRIL;
typedef enum {
NO_ERROR = 0,
SYNC_ERROR = 1,
POWER_ERROR = 2,
BUS_ERROR = 3,
/* More enums */
} Error_e;
Error_e error = NO_ERROR;
Unions
Derived data type containing multiple data members that occupy the same address
- unions can contain multiple members, each can be differenct types and sizes
- size of a union is equal to largest member
union
typedef union {
uint8_t x;
uint8_t y;
uint8_t z;
} ex1;
sizeof(ex1) // 1Byte
ex1 point;
point.x = 0x15;
typedef union {
uint8_t x;
uint16_t y;
uint32_t z;
uin8_t array[16];
} ex;
sizeof(ex) // 16 bytes
&ex = &ex.x = &ex.y = &ex.z = &ex.array[0];
typedef struct {
uint8_t x;
uint8_t y;
uint8_t z;
} Str1_t;
typedef struct {
uint32_t x;
uint32_t y;
uint32_t z;
} Str2_t;
typedef union {
Str1_t s1;
Str2_t s2;
} ex3;
sizeof(ex3) // 12-16 bytes
ex3 ex;
ex.s1.x = 0x12;
ex.s2.z = 0x12345678;
Format specifier
%[flags][width][.precision][length]specifier
| flags | description |
|---|---|
- |
Left-justify within the given field width; Right justification is the default (see width sub-specifier). |
+ |
Forces to preceed the result with a plus or minus sign (+ or -) even for positive numbers. |
| By default, only negative numbers are preceded with a - sign. | |
(space) |
If no sign is going to be written, a blank space is inserted before the value. |
# |
Used with o, x or X specifiers the value is preceeded with 0, 0x or 0X respectively for values different than zero. |
| Used with a, A, e, E, f, F, g or G it forces the written output to contain a decimal point even if no | |
| more digits follow. By default, if no digits follow, no decimal point is written. | |
0 |
Left-pads the number with zeroes (0) instead of spaces when padding is specified (see width sub-specifier). |
| width | description |
|---|---|
(number) |
Minimum number of characters to be printed. If the value to be |
| printed is shorter than this number, the result is padded with blank spaces. | |
| The value is not truncated even if the result is larger. | |
* |
The width is not specified in the format string, but as an additional |
| integer value argument preceding the argument that has to be formatted. |
| specifier | Output | Example |
|---|---|---|
d or i |
Signed decimal integer | 392 |
u |
Unsigned decimal integer | 7235 |
o |
Unsigned octal | 610 |
x |
Unsigned hexadecimal integer | 7fa |
X |
Unsigned hexadecimal integer (uppercase) | 7FA |
f |
Decimal floating point, lowercase | 392.65 |
F |
Decimal floating point, uppercase | 392.65 |
e |
Scientific notation (mantissa/exponent), lowercase | 3.9265e+2 |
E |
Scientific notation (mantissa/exponent), uppercase | 3.9265E+2 |
g |
Use the shortest representation: %e or %f | 392.65 |
G |
Use the shortest representation: %E or %F | 392.65 |
a |
Hexadecimal floating point, lowercase | -0xc.90fep-2 |
A |
Hexadecimal floating point, uppercase | -0XC.90FEP-20 |
c |
Character | a |
s |
String of characters | sample |
p |
Pointer address | b8000000 |
n |
Nothing printed. | |
| The corresponding argument must be a pointer to a signed int. | ||
| The number of characters written so far is stored in the pointed location. | ||
% |
A % followed by another % character will write a single % to the stream. | % |
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf ("Characters: %c %c \n", 'a', 65);
// Characters: a A
printf ("Decimals: %d %ld\n", 1977, 650000L);
// Decimals: 1977 650000
printf ("Preceding with blanks: %10d \n", 1977);
// Preceding with blanks: 1977
printf ("Preceding with zeros: %010d \n", 1977);
// Preceding with zeros: 0000001977
printf ("Some different radices: %d %x %o %#x %#o \n", 100, 100, 100, 100, 100);
// Some different radices: 100 64 144 0x64 0144
printf ("floats: %4.2f %+.0e %E \n", 3.1416, 3.1416, 3.1416);
// floats: 3.14 +3e+000 3.141600E+000
printf ("Width trick: %*d \n", 5, 10);
// Width trick: 10
printf ("%s \n", "A string");
// A string
return 0;
}
Bitwise operation
- Bitwise AND (&): This operation sets a bit to 1 only if both corresponding bits are 1.
-
Bitwise OR ( ): This operation sets a bit to 1 if either of the corresponding bits is 1. - Bitwise XOR ( ^ ): This operation sets a bit to 1 if the corresponding bits are different.
- Bitwise NOT ( ~ ): This operation flips each bit (0 to 1 and 1 to 0).
- Left Shift ( « ): This operation shifts the bits of a number to the left by a specified number of positions.
- Right Shift ( » ): This operation shifts the bits of a number to the right by a specified number of positions.
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
unsigned int a = 60; // 0011 1100 in binary
unsigned int b = 13; // 0000 1101 in binary
unsigned int result;
// Bitwise AND
result = a & b; // 0000 1100
printf("a & b = %d\n", result);
// Bitwise OR
result = a | b; // 0011 1101
printf("a | b = %d\n", result);
// Bitwise XOR
result = a ^ b; // 0011 0001
printf("a ^ b = %d\n", result);
// Bitwise NOT
result = ~a; // 1100 0011
printf("~a = %d\n", result);
// Left Shift
result = a << 2; // 1111 0000
printf("a << 2 = %d\n", result);
// Right Shift
result = a >> 2; // 0000 1111
printf("a >> 2 = %d\n", result);
return 0;
}
Bit Masks
Bit Masks are constant expressions used to set, clear, or toggle a specific set of bits
// Macros get replaced into the code by their corresponding values during pre processing and do not take up space in code memory
#define MASK1 (0x30) // 0011 0000
#define MASK2 (0xC0) // 1100 0000
#define MASK3 (0x0E) // 0000 1110
uint8_t foo = 0x0C; // 0000 1100
foo |= MASK1; // 0011 1100 // 0x3C
foo &= MASK2; // 0000 0000 // 0x00
foo ^= MASK3; // 0000 0010 // 0x02
construt type
int a[10]array- strut
- enum
- union
// this is a comment
/*
* this is a multi-line comment
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
void stringDisplay()
{
char color[20];
char pluralNoun[20];
char celebrityF[20];
char celebrityL[20];
printf("Enter a color: ");
scanf("%s", color);
printf("Enter a plural noun: ");
scanf("%s", pluralNoun);
printf("Enter a celebrity: ");
scanf("%s%s", celebrityF, celebrityL);
printf("Roses are %s\n", color);
printf("%s are blue\n", pluralNoun);
printf("I love %s %s\n", celebrityF, celebrityL);
}
typedef enum Color {
COLOR_BLUE = 0,
COLOR_RED = 1,
COLOR_GREEN = 2,
} Color_t;
typedef struct Data {
int32_t temperature;
uint32_t date;
uint32_t time;
} Data_t;
void arrayDisplay()
{
int luckyNumbers[] = {1, 3, 5, 7, 11, 17, 19, 23};
// luckyNumbers[1] = 200;
printf("%d\n", luckyNumbers[1]);
}
void invokeFunc()
{
printf("Hello World!\n");
}
double cube(double num)
{
double result = num * num * num;
return result;
}
void calculate()
{
double num1;
double num2;
char op;
printf("Enter a number: ");
scanf("%lf", &num1);
printf("Enter operator: ");
scanf(" %c", &op);
printf("Enter a number: ");
scanf("%lf", &num2);
if (op == '+')
{
printf("%f", num1 + num2);
}
else if (op == '-')
{
printf("%f", num1 - num2);
}
else if (op == '*')
{
printf("%f", num1 * num2);
}
else if (op == '/')
{
printf("%f", num1 / num2);
}
else
{
printf("Invalid operator!\n");
}
printf("\n");
}
void switchCondition()
{
char grade = 'A';
switch (grade)
{
case 'A':
printf("You did great!");
break;
case 'B':
printf("You did alright!");
break;
case 'C':
printf("You did poorly!");
break;
case 'D':
printf("You did very bad");
break;
case 'F':
printf("You Failed!");
break;
default:
printf("Invalid grade");
}
printf("\n");
}
struct Student
{
char name[50];
char major[50];
int age;
double gpa;
};
void useStruct()
{
struct Student student1;
student1.age = 22;
student1.gpa = 3.2;
strcpy(student1.name, "Johnson");
strcpy(student1.major, "eecs");
printf("%s\n", student1.name);
printf("%s\n", student1.major);
struct Student student2;
student2.age = 33;
student2.gpa = 5.6;
strcpy(student2.name, "Carlson");
strcpy(student2.major, "IOT");
printf("%s\n", student2.name);
printf("%s\n", student2.major);
}
void whileLoop()
{
int index = 1;
while (index <= 5)
{
printf("%d \n", index);
index++;
}
}
void doWhileLoop()
{
int index = 0;
do
{
printf("%d\n", index);
index++;
} while (index <= 5);
}
void loop()
{
int secretNumber = 5;
int guess;
int guessCount = 0;
int guessLimit = 3;
int outOfGuesses = 0;
while (guess != secretNumber && outOfGuesses == 0)
{
if (guessCount < guessLimit)
{
printf("Enter a number: ");
scanf("%d", &guess);
guessCount++;
}
else
{
outOfGuesses = 1;
}
}
if (outOfGuesses == 0)
{
printf("You Win!");
}
else
{
printf("You lose!");
}
}
void forLoop()
{
int luckyNumbers[] = {1, 3, 5, 7, 11};
int i;
printf("%d\n", sizeof(luckyNumbers));
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
printf("%d\n", luckyNumbers[i]);
}
/* loop forever */
for (;;);
}
long long factorialSum(int num)
{
long long result = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= num; i++)
{
long long pow = 1;
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++)
{
pow *= i;
}
result += pow;
printf("%d %lld\t %lld\n", i, pow, result);
}
return result;
}
void gotoPractice()
{
for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= 5; j++)
{
printf("inner loop executing %d\n", j);
// break; // exit inner loop
goto a;
}
printf("inner loop done\n");
}
// 标号
a: printf("outer loop done\n");
}
void array()
{
int nums[4][2] = {
{1, 2},
{3, 4},
{5, 6},
{7, 8},
};
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < 2; j++)
{
printf("nums[%d][%d]: %d\n", i, j, nums[i][j]);
}
}
}
void address()
{
int age = 30;
double gpa = 3.4;
char grade = 'A';
printf("age: %p\ngpa: %p\ngrade: %p\n", &age, &gpa, &grade);
}
void pointerAddress()
{
int age = 30;
int *pAge = &age;
double gpa = 3.4;
double *pGpa = &gpa;
char grade = 'A';
char *pGrade = &grade;
// printf("age's memory address: %p \n", pAge);
// dereferencing a pointer variable
printf("pointer's value: %d \n", *pAge);
// getting the physical address and then dereferencing it
printf("%d", *&age);
}
void writeFile()
{
// w => write
// a => append
FILE *fpointer = fopen("employees.txt", "a");
// write info to a file
fprintf(fpointer, "OVERRIDDEN!\nJim, Salesman\nPam, Receptionist\nOscar, Accounting\n");
fclose(fpointer);
}
void readFile()
{
char line[255];
// r => read
FILE *fp = fopen("employees.txt", "r");
// read file line by line
fgets(line, 255, fp);
fgets(line, 255, fp);
printf("%s", line);
fclose(fp);
}
void helloWorld()
{
printf("Hello World!\n");
}
void testChar()
{
printf("%c\n", 'a');
printf("%d\n", 'a');
printf("%c\n", '\0');
}
void testVariable()
{
// Student data
int studentID = 15;
int studentAge = 23;
float studentFee = 75.25;
char studentGrade = 'B';
// Print variables
printf("Student id: %d\n", studentID);
printf("Student age: %d\n", studentAge);
printf("Student fee: %f\n", studentFee);
printf("Student grade: %c\n", studentGrade);
int num1, num2;
printf("Please input two int: \n");
scanf("%d %d", &num1, &num2);
printf("You've entered: %d %d\n", num1, num2);
float sum = (float) 5 / 2;
printf("%f.1\n", sum);
const float PI = 3.14;
}
void testSign()
{
signed int num;
printf("%d output singed int\n", +32);
printf("%hd output singed short\n", -2);
printf("%ld output singed long\n", -6553589102);
unsigned int num2;
printf("%u ouput unsigned int\n", 32);
printf("%hu output unsinged short\n", 2);
printf("%lu output unsigned long\n", 6553589102);
}
void testNumber()
{
// Octal 八进制
// hexadecimal 十六进制
// true form 原码
// base minus one's complement 反码
// Complement Code 补码
// negative number are saved in Complement Code
// non-negative number are saved in true form
// octal in true form
// hexadecimal in true form
char ch1 = -10;
printf("ch1=%#x\n", ch1);
// ch1=0xfffffff6
char ch2 = 6;
printf("ch2=%#x\n", ch2);
// ch2=0x6
unsigned char ch = -10;
printf("%#x\n", ch); // 0xf6
printf("%d\n", ch); // 246
printf("%u\n", ch); // 246
// read-only variable initialize
const int num = 100;
// register variable
// cannot use &freq
register int freq = 10;
// volatile
// 1.强制访问内存
// 2.防止编译器优化
// 3.sizeof测量类型大小
volatile int force = 10;
}
void testSizeOf()
{
int num = 0;
printf("%lu\n", sizeof(num)); // 4
printf("%lu\n", sizeof(int)); // 4
printf("%lu\n", sizeof(short)); // 2
printf("%lu\n", sizeof(long)); // 8
char ch = 'a';
printf("%lu\n", sizeof(ch)); // 1
printf("%lu\n", sizeof('a')); // 4 (ASCII)
}
// typedef
// 给已有类型重新取别名
// 1.不能创建新类型
// 2.旧类型任然可用
void testTypeDef()
{
typedef int MY_ARRAY[5];
MY_ARRAY arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i<5; i++)
{
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
/**
* type auto change: ensure accuracy
* low => high
* char,short => signed int => unsigned int => long => double
* float => double
*/
void testTypeChange()
{
int data1 = -10;
unsigned int data2 = 6;
if (data1 + data2 > 0)
{
printf(">0");
}
else
{
printf("<0");
}
// >0
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
helloWorld();
testChar();
testVariable();
testSign();
testNumber();
testSizeOf();
testTypeDef();
testTypeChange();
// stringDisplay();
// arrayDisplay();
// invokeFunc();
// printf("Answer: %f\n", cube(3.0));
// calculate();
// switchCondition();
// useStruct();
// whileLoop();
// doWhileLoop();
// loop();
// forLoop();
// array();
// address();
// pointerAddress();
// writeFile();
readFile();
return 0;
return 0;
}
Strutctures 2
// memory alignment
struct stuct_name {
int8_t var1;
int8_t var2;
int32_t var3;
} __attribute__((packed));
// Create a structure called myStructure
struct myStructure {
char myLetter;
char myString[30]; // String
int myNum;
};
struct Car {
char brand[50];
char model[50];
int year;
};
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
// Create a structure variable of myStructure called s1
struct myStructure s1;
// Assign values to members of s1
s1.myNum = 13;
s1.myLetter = 'B';
// Assign a value to the string using the strcpy function
strcpy(s1.myString, "Some text");
// Print values
printf("My number: %d\n", s1.myNum);
printf("My letter: %c\n", s1.myLetter);
printf("My string: %s", s1.myString);
struct Car car1 = {"BMW", "X5", 1999};
struct Car car2 = {"Ford", "Mustang", 1969};
printf("%s %s %d\n", car1.brand, car1.model, car1.year);
return 0;
}
Escape Characters
| escape character | meaning |
|---|---|
\n |
New line |
\t |
Tab |
\0 |
Null |
\0 |
ASCII 0 |
\r |
to line start |
\a |
alert |
- octal escape
\ddd
each d range 0~7, max 3 octal digit in total
- hexadecimal escap
\xhh
each h range 0~9, a~f, max 2 hex digit in total
#include <string.h>
char alphabet[] = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ";
printf("%d", strlen(alphabet)); // 26
printf("%d", sizeof(alphabet)); // 27
// sizeof also includes the `\0` character when counting
char alphabet[50] = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ";
printf("%d", strlen(alphabet)); // 26
printf("%d", sizeof(alphabet)); // 50
// sizeof will always return the memory size (in bytes), and not the actual string length
char str1[20] = "Hello ";
char str2[] = "World!";
strcat(str1, str2);
// Print str1
printf("%s", str1);
char str1[20] = "Hello World!";
char str2[20];
// Copy str1 to str2
strcpy(str2, str1);
printf("%d\n", strcmp(str1, str2)); // Returns 0 (the strings are equal)
User input
// Create an integer variable that will store the number we get from the user
int myNum;
// Ask the user to type a number
printf("Type a number: \n");
// Get and save the number the user types
scanf("%d", &myNum);
char firstName[30];
scanf("%s", firstName);
// you don't have to specify the reference operator (&) when working with strings in scanf()
// Output the number the user typed
printf("Your number is: %d", myNum);
char fullName[30];
printf("Type your full name: \n");
fgets(fullName, sizeof(fullName), stdin); // read a line of text
Memory Address VS Pointers
A pointer is a variable that stores the memory address of another variable. Instead of holding a data value directly, a pointer holds the address where the data is stored. This allows for indirect access and manipulation of the variable’s value.
All Pointers are the same length
uint8_t * ptr1 = (uint8_t *) 0x00;
uint16_t * ptr2 = (uint16_t *) 0x04;
uint32_t * ptr3 = (uint32_t *) 0x08;
float * ptr4 = (uint8_t *) 0x0C;
// 32-bits!!
sizeof(uint8_t*) = sizeof(uint16_t*) = sizeof(uint32_t*) = sizeof(float*)
// 32-bits!!
sizeof(ptr1) = sizeof(ptr2) = sizeof(ptr3) = sizeof(ptr4)
sizeof(*ptr1) // 1 Byte
sizeof(*ptr2) // 2 Bytes
sizeof(*ptr3) // 4 Bytes
sizeof(*ptr4) // 4 Bytes
data_type * pointer_name
* means:
- When used in declaration (
int* ptr), it creates apointer variable. - When not used in declaration, it act as a
dereference operator.
int myAge = 43;
printf("%p", &myAge); // Outputs 0x7ffe5367e044
// A pointer variable, with the name ptr, that stores the address of myAge
int* ptr = &myAge;
// Output the memory address of myAge with the pointer (0x7ffe5367e044)
printf("%p\n", ptr);
// Dereference: Output the value of myAge with the pointer (43)
printf("%d\n", *ptr);
// to assign a direct address to a pointer
// casts integer to address
// does not change the value of the address
// tells the compiler to interrupt this number as an address
uint16_t * ptr = (uint16_t *) 0x480C0000;
Pointers
- Deference Operator
*: accesses data at address - Address-of Operator
&: provides address of variable
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void demo()
{
int a = 10;
int* p = &a;
printf("%d\n", *p);
*p = 200;
printf("%d\n", *p);
printf("%d\n", a);
char c = 'a';
char* p1 = &c;
long long n = 100;
long long* p2 = &n;
printf("%zu\n", sizeof(p1)); // 8
printf("%zu\n", sizeof(p2)); // 8
}
void swap(int* p1, int* p2)
{
int temp = *p1;
*p1 = *p2;
*p2 = temp;
}
void demo2()
{
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
printf("Before swap: %d %d\n", a, b);
swap(&a, &b);
printf("After swap: %d %d\n", a, b);
}
void calcMaxAndMin(int arr[], int len, int* max, int* min)
{
for (int i = 1; i < len; i++)
{
if (arr[i] > *max)
{
*max = arr[i];
}
if (arr[i] < *min)
{
*min = arr[i];
}
}
}
void demo3()
{
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 };
int len = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(int);
int max = arr[0];
int min = arr[0];
calcMaxAndMin(arr, len, &max, &min);
printf("Max: %d Min: %d\n", max, min);
}
int getRemainder(int a, int b, int* res)
{
if (b == 0)
{
return 1;
}
*res = a % b;
return 0;
}
void demo4()
{
int a = 10, b = 3;
int res = 0;
int flag = getRemainder(a, b, &res);
if (!flag)
{
printf("Remainder: %d\n", res);
}
}
void demo5()
{
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 };
int* p = &arr[0];
printf("%d\n", *p);
printf("%d\n", *(p + 1));
int* p2 = &arr[5];
printf("%d\n", p2 - p);
printf("%p\n", p);
printf("%p\n", p2);
}
int* method()
{
int a = 100;
return &a;
}
void demo6()
{
int a = 10;
int* p = &a;
printf("%p\n", p);
printf("%d\n", *p);
// wild pointer;
int* p2 = p + 10;
printf("%p\n", p2);
printf("%d\n", *p2);
// empty pointer
int* p3 = method();
printf("take some other task and time spent\n");
printf("%d\n", *p3);
}
void generalSwap(void* p1, void* p2, int len)
{
char* pc1 = p1;
char* pc2 = p2;
char temp = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
temp = *pc1;
*pc1 = *pc2;
*pc2 = temp;
pc1++;
pc2++;
}
}
void demo7()
{
int a = 10;
short b = 20;
int* p1 = &a;
short* p2 = &b;
printf("%d\n", *p1);
printf("%d\n", *p2);
// void* p4 = p1;
// void* p5 = p2;
int* c = 100;
int* d = 200;
generalSwap(&c, &d, sizeof(int));
printf("c = %d, d = %d\n", c, d);
}
void demo8()
{
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
int* p = &a;
int** pp = &p;
*pp = &b;
printf("%p\n", &a);
printf("%p\n", &b);
printf("%p\n", p);
printf("%d\n", **pp);
}
/**
Arrays and pointers are closely related in C.
The name of an array is a constant pointer to its first element.
*/
void demo9()
{
// get array pointer address
int arr[] = { 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 };
int len = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(int);
int* p1 = arr;
int* p2 = &arr[0];
int* p3 = &arr;
printf("%zu\n", sizeof(arr)); // 20;
printf("%p\n", p1); // 000000C05E0FF8B8
printf("%p\n", p2); // 000000C05E0FF8B8
printf("%p\n", p3); // 000000C05E0FF8B8
printf("%p\n", arr + 1);
printf("%p\n", &arr + 1);
// Here, ptr is assigned the address of the first element of arr.
// You can use pointer arithmetic to traverse the array:
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
printf("%d\n", *p1++);
// printf("%d ", *(p1 + i));
}
}
void demo10()
{
int arr[3][5] =
{
{1, 2, 3, 4, 5},
{11, 22, 33, 44, 55},
{111, 222, 333, 444, 555},
};
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
{
printf("%d\t", arr[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("---------------\n");
int arr1[3] = { 1, 2, 3 };
int arr2[5] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
int arr3[9] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 };
int* arra[3] = {arr1, arr2, arr3};
int len1 = sizeof(arr1) / sizeof(int);
int len2 = sizeof(arr2) / sizeof(int);
int len3 = sizeof(arr3) / sizeof(int);
int lenArr[3] = { len1, len2, len3};
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
// int len = sizeof(arra[i]) / sizeof(int); // 2
for (int j = 0; j < lenArr[i]; j++)
{
printf("%d\t", arra[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
void demo11a()
{
int arr[3][5] =
{
{1, 2, 3, 4, 5},
{11, 22, 33, 44, 55},
{111, 222, 333, 444, 555},
};
printf("%p\n", arr);
printf("%p\n", arr + 1);
int(*p)[5] = arr;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
{
printf("%d\t", *(*p + j));
}
printf("\n");
p++;
}
}
void demo11b()
{
int arr1[5] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
int arr2[5] = { 11, 22, 33, 44, 55 };
int arr3[5] = { 111, 222, 333, 444, 555 };
int* arr[3] = { arr1, arr2, arr3 };
int** p = arr;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
{
printf("%d\t", *(*p + j));
}
printf("\n");
p++;
}
}
void methodA();
int methodB(int a, int b);
/**
* function pointer
*/
void demo12()
{
void (*a)() = methodA;
int (*b)(int, int) = methodB;
a();
int res = b(3, 4);
printf("%d\n", res);
}
int add(int a, int b)
{
return a + b;
}
int subtract(int a, int b)
{
return a - b;
}
int multiply(int a, int b)
{
return a * b;
}
int divide(int a, int b)
{
return a / b;
}
/**
* function pointer array
*/
void demo13()
{
int (*p[4])(int, int) = { add, subtract, multiply, divide };
int choose = 1;
printf("Please input two number: \n");
int num1;
int num2;
scanf("%d %d", &num1, &num2);
printf("%d\n", num1);
printf("%d\n", num2);
printf("Please input a number to operate(1~4): \n");
scanf("%d", &choose);
int res = (p[choose - 1])(num1, num2);
printf("Result: %d\n", res);
}
void userInput(float * num1, float * num2, float* num3, float* num4)
{
printf("Enter the first number: ");
fflush(stdout);
scanf("%f", num1);
printf("\nEnter the second number: ");
fflush(stdout);
scanf("%f", num2);
printf("\nEnter the third number: ");
fflush(stdout);
scanf("%f", num3);
printf("\nEnter the fourth number: ");
fflush(stdout);
scanf("%f", num4);
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
// demo();
// demo2();
// demo3();
// demo4();
// demo5();
// demo6();
// demo7();
// demo8();
// demo9();
// demo10();
// demo11a();
// demo11b();
// demo12();
// demo13();
float num1, num2, num3, num4;
float avg;
userInput(&num1, &num2, &num3, &num4);
avg = (num1 + num2 + num3 + num4)/4;
printf("Average is: %f\n", avg);
printf("Press any key to exit the application");
getchar();
getchar();
}
void methodA()
{
printf("methodA\n");
}
int methodB(int a , int b)
{
printf("methodB\n");
return a + b;
}
Null Pointers
At time of pointer declaration, you might not know the address
- Null pointers point to nothing, used to check for valid pointer
- Deferencing a NULL pointer can cause an exception
// this pointer will have garbage data
uint32_t * ptr;
#define NULL((void*)0)
uint32_t * ptr = NULL;
if (ptr == NULL)
{
/* error */
}
*ptr = 0xABCD1234;
Endianness
/* Switches endinannes of variable pointed by ptr */
void byte_swap32(uint32_t * ptr)
{
uint8_t i, temp_byte;
for (i=0; i<2; i++)
{
temp_byte = *((uint_t*)ptr + (3-i));
*((uint8_t*)ptr + (3-i)) = *((uint8_t*)ptr + i)
*((uint8_t*)ptr + i) = temp_byte;
}
}
/* Assume little endian */
void main()
{
uint32_t var = 0xABCD1234;
uint32_t * ptr = &var;
byte_swap32(ptr);
while(1);
}
volatile
- tells compiler NOT to optimize this code
- volatile variable needs to be directly read and written when specified
Structure overlay
Define a Structure to directly match peripherl region registers
- require exact replica of peripheral region
- size registers to equivalent standard types
- order matters
- leave space for reserved bytes
- Read-Only Registers = Const!
- All registers are volatile
typedef struct {
__IO uint16_t CTL;
__IO uint16_t CTTL[7];
__IO uint16_t R;
__IO uint16_t CCR[7];
__IO uint16_t EX0;
uint16_t RESERVED0[6];
__I uint16_t IV;
} Timer_A_Type;
#define __IO(volatile)
#define __I(volatile const)
/* Define the base address of peripheral regions */
#define PERIPH_BASE ((uint32_t)0x40000000)
#define TIMER_A0_BASE (PERIPH_BASE + 0x00000000)
#define TIMER_A1_BASE (PERIPH_BASE + 0x00000400)
#define TIMER_A2_BASE (PERIPH_BASE + 0x00000800)
/* Multiple Timer modules, different addresses */
#define TIMER_A0 ((Timer_A_Type *)TIMER_A0_BASE)
#define TIMER_A1 ((Timer_A_Type *)TIMER_A1_BASE)
#define TIMER_A2 ((Timer_A_Type *)TIMER_A2_BASE)
// Example use of Structure overlay:
TIMER_A0->CTL = 0x0202;
Macro Functions
Direct substitution in code
#define TA0CTL_ADDR (0x40000000)
/* 8, 16, & 32 Bit Register Access Macros */
#define HWREG8(x) (*((volatile uint8_t *)(x)))
#define HWREG16(x) (*((volatile uint16_t *)(x)))
#define HWREG32(x) (*((volatile uint32_t *)(x)))
#define TA0CTL (HWREG16(0x40000000))
/* example use of access methods: */
HWREG16(TA0CTL_ADDR) = 0x0202;
// SAME AS
(*((volatile uint16_t *)(0x40000000))) = 0x0202;
/* example use of access macro */
TA0CTL = 0x0202;
// SAME AS
volatile uint16_t * ta0_ctl = (uint16_t*)TA0CTL_ADDR;
*ta0_ctl = 0x0202;
PORT MACROS
/* Port 1 Register Access Macros */
#define P1IN (HWREG8(0x40004C00))
#define P1OUT (HWREG8(0x40004C02))
#define P1DIR (HWREG8(0x40004C04))
#define P1SEL0 (HWREG8(0x40004C0A))
#define P1SEL1 (HWREG8(0x40004C0C))
#define P1IES (HWREG8(0x40004C18))
#define P1IE (HWREG8(0x40004C1A))
/* set P1.0 to output direction */
P1DIR |= 0x01;
typedef struct {
__I uint8_t IN;
uint8_t RESERVED0;
__IO uint8_t OUT;
uint8_t RESERVED1;
__IO uint8_t DIR;
uint8_t RESERVED2;
__IO uint8_t REN;
uint8_t RESERVED3;
/* ... MORE REGISTERS */
} DIO_PORT_TYPE;
/* Define the PORT Constants and Types */
#define PIN0(0x0)
#define DIO_PORT1_ADDR ((uint32_t)0x40004C00)
#define P1((DIO_PORT_TYPE*)(DIO_PORT1_ADDR))
#define SET_PORT_PIN_DIR (port, pin) ((port)->DIR |= (1<<pin))
/* set P1.0 to output direction */
SET_PORT_PIN_DIR(P1, PIN0)
Bit Band Macros
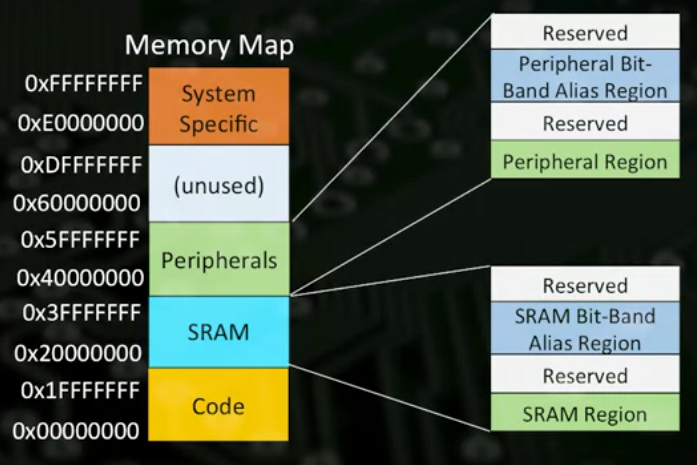
- Bit Band Region allows for atomic reads/writes of single bits for first 1MB of SRAM and Peripheral Memory
- Not all of the SARM & Peripheral Memory has a bit-band alias
#define TA0CTL_ADDR(0x40000000)
/* Bit Band Region is offset from Peripheral/SRAM */
#define BB_OFFSET(0x02000000)
/* Macro Function to Read Memory */
#define HWREG32(addr)(*((volatile uint32_t *)(addr)))
/* Bit Band Alias Offset Address */
#define BITBAND_ADDR(addr, bit)((addr & 0xF0000000) + BB_OFFSET + \
((addr & 0xFFFFF) << 5) + (bit << 2))
/* Set bit 1 of TA0CTL Register */
HWREG32(BITBAND_ADDR(TA0CTL_ADDR, 1))
Macro problems
- No Type Checking
- Bug Introduction
- Complex/Confusing Layers of Macros Calling Macros
- Code Size and Duplication
// Directive used for Boolean Compilation Conditions
/* Define feature for the MSP */
#define MSP_PLATFORM
#define TEN (10)
/* undefine the feature */
#undef TEN
#define COMPILE_CODE
// ...
#ifdef COMPILE_CODE
// Code will be compiled
#endif
#define DO_NOT_COMPILE_CODE
// ...
#undef DO_NOT_COMPILE_CODE
#ifdef DO_NOT_COMPILE_CODE
// Code will NOT be compiled
#endif
Compile Time switch
Condition provided at Compile time to dicate WHAT should be compiled, by use combination of #if-else and #define directives, for the following example: Add extra option to gcc command to deinfe Macro
# -D<MACRO-NAME>
gcc -DMSP_PLATFORM -o main.out main.c
#if defined ( KL25_PLATFROM ) && !defined ( MSP_PLATFORM)
kl25_init();
#elif defined ( MSP_PLATFORM ) && !defined( KL25_PLATFROM )
msp_init();
#else
#error "Plaese specify one platfrom target"
#endif
Specialized C Functions
- Functions are excellent for encapsulating a specialized operation
- Calling a traditional C-function can decrease performance due to calling convention overhead
inline Keyword
Skips calling convention, copies function body into calling code
inlinea c99 Feature -> Not supported in c89always_inlineis a GCC attribute -> Not supported in other compilers- Good for small functions
- Bad for Recursive/Variadic/Long functions
- Functions with the
inlinekeyword allow C programming type checking, a suggestion and functions may not be inlined
__attribute__((always_inline)) inline int32_t add(int32_t x, int32_t y)
{
return (x+y);
}
static keyword
static keyword can apply to functions to create private access
- Function/Variable only visible to current file
- Combine
staticandinlineto prevent integrating all code into calling function - Linkage is interal to file
/* core_cm4.h */
__attribute__((always_inline)) static inline void __enable_irq(void)
{
__ASM volatile ("cpsie i":::"memory");
}
Interface Libray for GPIO
/* IO_MSP432.h */
#include <stdio.h>
#include "msp.h"
__attribute__((always_inline)) static inline void IO_Read(DIO_PORT_TYPE * port, uint8_t pin)
{
return (((port)->IN) & (1<<pin));
}
__attribute__((always_inline)) static inline void IO_Write(DIO_PORT_TYPE * port, uint8_t pin, uint8_t value)
{
value ? (((port)->OUT) |= (1<<pin)) : (((port)-> OUT) &= ~(1<<pin));
}
/* Platform.h */
#if defined (KL25Z) && !defined (MSP432)
#inclue "IO_KL25Z.h"
#elif defined(MSP432) && !defined (KL25Z)
#inclue "io_msp432.h"
#else
#error "Platform not properly specified"
#endif
make all PLATFORM=MSP432
Advanced Pointers
Memories of an Embedded System
- Generic Pointer(void)
- Double Pointer
- Restrict Pointer
void * ptr1 = NULL;
void ** ptr2 = &ptr1;
uint32_t * restrict ptr3;
uint32_t ** ptr4;
sizeof (uint8_t *) = sizeof (void *)
= sizeof (void **)
= sizeof (uint32_t **)
= sizeof (uint32_t * restrict)
// = 32 bits
sizeof(ptr1) = sizeof(ptr2)
= sizeof(ptr3)
= sizeof(ptr4)
// = 32 bits
Void Pointer
Void pointers are Generic Pointers, they point to a memory address
void= Lack of type, dereferencing does not make sense!- Must cast before using
- No dereferencing on a void *
- No pointer arithmetic on a void *
- Void pointers are NOT NULL pointers, but a NULL Pointer is a void point
mallocreserves blocks of data, it does not care how it is usedmallocreturns a void pointer, you cast this pointer for the intended use
#define NULL(void *(0))
void *ptr1 = NULL;
void * ptr1 = (void*)0x40000000;
*((uint16_t*)ptr1) = 0x0202;
// equivalent to:
TA0CTL = 0x0202;
char * ptr;
ptr = (char *)malloc(8*sizeof(char));
if (ptr == NULL)
{
/* Allocation Failed!! */
/* ...Handle Failure */
}
/* Other code */
free((void*)ptr);
Double Pointer
Double pointers are a pointer to a pointer, This is useful for multidimensional arrays or dynamic memory management.
- must use the
**in declarations - used to set value of a pointer (address)
- single dereference accesses pointer address
- double dereference accesses pointer data
- copies of pointers are made when passed into a function
- original pointer address cannot be altered!
uint32_t var = 0x1234ABCD;
uint32_t * ptr3 = &var;
uint32_t ** ptr4 = &ptr3;
sizeof (float **) = sizeof(uint8_t**)
= sizeof(void **)
= sizeof(uint32_t **)
// = 32 bits
typedef enum {
RSP_TYPE_1 = 0,
RSP_TYPE_2 = 1,
} RSP_e;
typedef struct {
RSP_e rsp_type;
uint8_t data[4];
} rsp1;
int8_t create_rsp1 (rsp1 ** r_p)
{
*r_p = (rsp1 *)malloc (sizeof(rsp1));
if (*r_p == NULL)
{
/* allocation failed */
return -1;
}
(*r_p)-> rsp_type = RSP_TYPE_1;
return 0;
}
int value = 10;
int *ptr = &value;
int **ptr_to_ptr = &ptr;
// Here, ptr_to_ptr holds the address of ptr, which in turn holds the address of value.
Dynamic Memory Allocation
Pointers are essential for dynamic memory allocation, which allows you to allocate memory at runtime. The standard library functions
malloc(),calloc(),realloc(), andfree()are used for this purpose.
malloc(size_t size): Allocates size bytes of memory and returns a pointer to the allocated memory.calloc(size_t num, size_t size): Allocates memory for an array of num elements, each of size bytes, and initializes all bytes to zero.realloc(void *ptr, size_t size): Changes the size of the memory block pointed to by ptr to size bytes.free(void *ptr): Deallocates the memory previously allocated by malloc(), calloc(), or realloc().
int *arr = (int *)malloc(5 * sizeof(int));
if (arr == NULL) {
// Handle memory allocation failure
}
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
arr[i] = i + 1;
}
free(arr);
// This code allocates memory for an array of 5 integers, initializes the array, and then deallocates the memory.
Restrict Qualified Pointer
Restrict type qualifier helps compiler to optimize memory interactions
- introduced in C99 Standard
- Only the data at this location or data near is accessed by this pointer
- Largest speedup comes from iteractive memory interaction
uint32_t * restrict ptr4;
sizeof (float *) = sizeof(uint8_t*)
= sizeof(void *)
= sizeof(uint32_t * restrict)
// = 32 bits
Function Pointers
Pointers can also point to functions. This allows you to pass functions as arguments to other functions or store them in data structures. Function pointers are declared using the function’s signature.
- defined just like a function (return type/function parameters/pointer name)
- Dereferencing a function pointer will call a function
- Dereferencing a function pointer gives us access to code memory
- declaration requires parentheses and a pointer
* -
(* )( ) = ; - initialization and dassignment to a function pointer should have matching return types and parameter list
- function pointers can be declared with an array
int add(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
int (*func_ptr)(int, int) = &add;
printf("Result: %d\n", func_ptr(2, 3));
// Here, func_ptr is a pointer to the add function, and it is used to call the function.
/* A function pointer variable declaration that returns a int8_t type */
int8_t (*foo)();
/* A function declaration that return a int8_t pointer type */
int8_t *foo();
// more function pointer examples
int8_t void (*bar)(int8_t a, int8_t *b);
uint32_t (* func)(uint8_t param);
sizeof (void(*)) = sizeof(void *)
= sizeof(uint32_t *)
// = 32 bits
// call
(* foo)();
// or
foo();
/* Function bar prototype */
int8_t bar();
/* function pointer */
int8_t (*foo)() = &bar;
// function pointer array
typedef void (* FuncPtr_t[2])();
FuncPtr_t example =
{
foo,
bar
};
// alternatively
typedef void (* FuncPtr_t());
FuncPtr_t example[2] =
{
foo,
bar
}
typedef enum
{
FP_FOO = 0,
FP_BAR = 1,
} FP_e;
// example calls:
example[FP_FOO]();
example[FP_BAR]();
Interrupt vector table
Interrupts are special events that request the CPU to perform a specific operation
- Interrupt Service Routine: Function to be called in response to an interrupt request
- Vector table definition requires both linker mapping and C/assembly code
- vector table is an array of function addresses, used to “jump” into a routine when interrupt occurs
- the interrupt vector table is an array of function pointers that are indexed according to priority.
Common Pitfalls and Best Practices
Using pointers comes with certain risks and challenges. Here are some common pitfalls and best practices to keep in mind:
- Uninitialized Pointers: Always initialize pointers before using them. Uninitialized pointers contain garbage values and can lead to undefined behavior.
- Dangling Pointers: Avoid using pointers that point to memory that has been deallocated. This can lead to crashes or corrupt data.
- Null Pointers: Check if a pointer is NULL before dereferencing it. This prevents accessing invalid memory.
- Pointer Arithmetic: Be cautious with pointer arithmetic. Ensure that you do not access memory outside the bounds of the allocated memory.
- Memory Leaks: Always deallocate dynamically allocated memory using free() to prevent memory leaks.
- Type Safety: Ensure that pointers point to the correct data type to prevent type mismatches and unexpected behavior.
Advanced Pointer Topics
- Pointer Arrays: Arrays of pointers are used for dynamic lists, such as an array of strings (array of char*).
- Pointer Casting: You can cast pointers from one type to another, but do so with caution to avoid undefined behavior.
- Function Pointers in Structures: Function pointers can be included in structures to implement callback mechanisms or function tables.
- Memory Mapping: Pointers are used in systems programming for memory-mapped I/O, where hardware registers are accessed through specific memory addresses.
The stdint.h header file defines fixed-width integer types such as int8_t, uint8_t, int16_t, uint16_t, int32_t, uint32_t, int64_t, and uint64_t. These types ensure that integers have a specific width (in bits) across different platforms, which is crucial for portability and reliability in embedded systems.
Operator
Operator Precedence
Bitwise operation
Bitwise operators perform operations on the binary representations of data. Unlike arithmetic operators that work on entire values, bitwise operators manipulate individual bits of the operands. The primary bitwise operators in C are:
- AND (&)
-
OR ( ) - EXOR (^)
- One’s Complement (~)
- Left Shift («)
- Right Shift (»)
applications cases are:
- Testing of bits
& - Setting of bits
| - Clearing of bits
~ and & - toggling of bits
^
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int num;
printf("Please enter a number");
scanf("%d", &num);
if (num & 1)
printf("%d is odd number\n", num);
else
printf("%d is even number\n", num);
int x = 0x7b;
printf("%#x", x);
// 0x7b
x ^= (1 << 5); // toggle the fifth bit of a variable x
printf("%#X", x);
// 0X5B
x &= ~(1 << 4); // clear the fourth bit of a variable x
printf("%#X", x);
// 0X4B
int a = 12; // Binary: 1100
int b = 10; // Binary: 1010
int result = a & b; // Binary: 1000, Decimal: 8
int result = a | b; // Binary: 1110, Decimal: 14
int result = a ^ b; // Binary: 0110, Decimal: 6
int a = 12; // Binary: 00001100
int result = ~a; // Binary: 11110011, Decimal: -13 (in 2's complement form)
int a = 12; // Binary: 1100
int result = a << 2; // Binary: 110000, Decimal: 48
int a = 12; // Binary: 1100
int result = a >> 2; // Binary: 0011, Decimal: 3
uint8_t * ptr = (uint8_t*)0x1000;
// set 4th bit without changing other bits:
*ptr |= 0x10
// clear 4th bit without changing other bits:
*ptr &= ~(0x10)
// toggle 4th bit
*ptr ^= 0x10
return 0;
}
Setting a Bit: To set a specific bit to 1, use the OR operator with a bitmask.
int num = 10; // Binary: 1010
int bit_to_set = 1; // Set the second bit (from the right)
num |= (1 << bit_to_set); // Result: 1010 | 0010 = 1110 (Decimal: 14)
Clearing a Bit: To clear a specific bit to 0, use the AND operator with a bitmask.
int num = 14; // Binary: 1110
int bit_to_clear = 1; // Clear the second bit (from the right)
num &= ~(1 << bit_to_clear); // Result: 1110 & 1101 = 1100 (Decimal: 12)
Toggling a Bit: To toggle a specific bit, use the XOR operator with a bitmask.
int num = 10; // Binary: 1010
int bit_to_toggle = 1; // Toggle the second bit (from the right)
num ^= (1 << bit_to_toggle); // Result: 1010 ^ 0010 = 1000 (Decimal: 8)