I/O Port
Quasi-bidirectional I/O
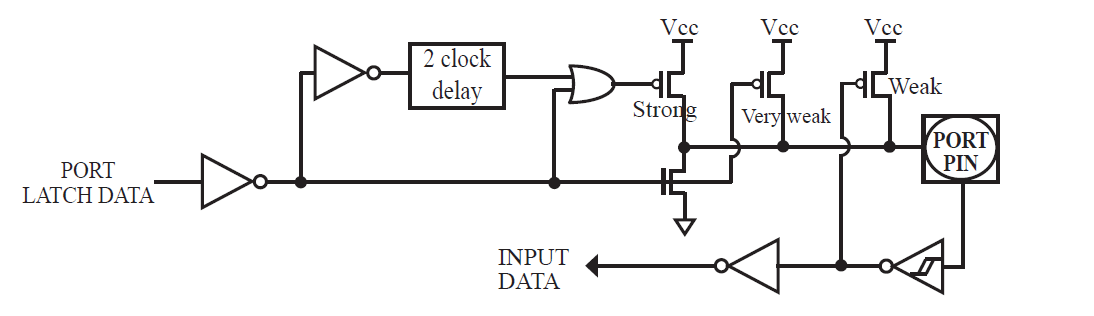
A quasi-bidirectional port can be used as an input and output without the need to reconfigure the port. This is possible because when the port outputs a logic high, it is weakly driven, allowing an external device to pull the pin low. When the pin outputs low, it is driven strongly and able to sink a large current. There are three pull-up transistors in the quasibidirectional output that serve different purposes. One of these pull-ups, called the “very weak” pull-up, is turned on whenever the port register for the pin contains a logic “1”. This very weak pull-up sources a very small current that will pull the pin high if it is left floating. A second pull-up, called the “weak” pull-up, is turned on when the port register for the pin contains a logic “1” and the pin itself is also at a logic “1” level. This pull-up provides the primary source current for a quasibidirectional pin that is outputting a 1. If this pin is pulled low by the external device, this weak pull-up turns off, and only the very weak pull-up remains on. In order to pull the pin low under these conditions, the external device has to sink enough current to over-power the weak pull-up and pull the port pin below its input threshold voltage. The third pull-up is referred to as the “strong” pull-up. This pull-up is used to speed up low-to-high transitions on a quasi-bidirectional port pin when the port register changes from a logic “0” to a logic “1”. When this occurs, the strong pull-up turns on for two CPU clocks, quickly pulling the port pin high.
Push pull output
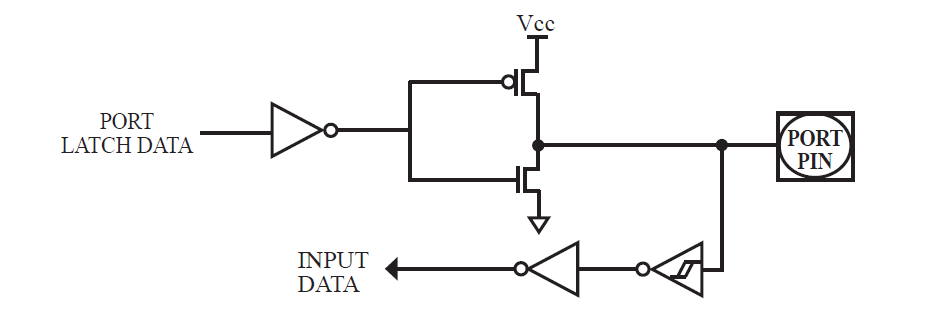
The push-pull output configuration has the same pull-down structure as both the open-drain and the quasibidirectional output modes, but provides a continuous strong pull-up when the port register conatins a logic “1”. The push-pull mode may be used when more source current is needed from a port output. In addition, input path of the port pin in this configuration is also the same as quasi-bidirectional mode.
Input-only Mode
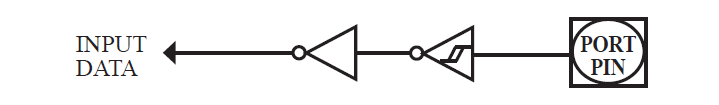
The input-only configuration is a Schmitt-triggered input without any pull-up resistors on the pin.
Open drain output
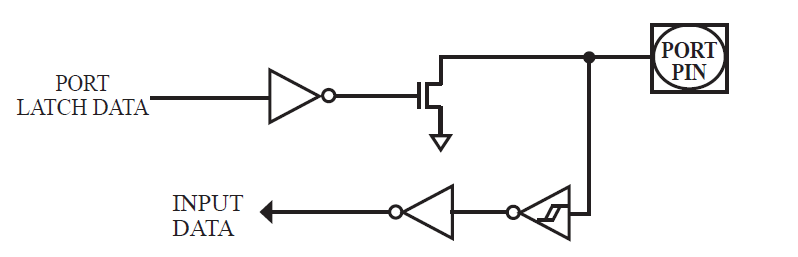
The open-drain output configuration turns off all pull-ups and only drives the pull-down transistor of the port pin when the port register contains a logic “0”. To use this configuration in application, a port pin must have an external pull-up, typically tied to VCC. The pull-down for this mode is the same as for the quasi-bidirectional mode. The input path of the port pin in this configuration is the same as quasibidirection mode.
Page Source