Artifical Intelligence
Terminology
Neurons
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Vanilla | Basic unit computing weighted sum + activation; used in FFNNs and CNNS |
| LSTM | Advanced neuron with memory and gates for long-term dependencies in sequences |
Layers
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Fully Connected | Standard layer where each neuron connects to all inputs |
| Recurrent | Maintains memory across timesteps; used in RNNs, LSTMs |
| Convolutional | Extracts spatial features using filters; used in image data |
| Attention | Computes weighted importance of different inputs; key in Transformers |
| Pooling | Downsamples spatial data; used in CNNs to reduce size and noise |
| Normalization | Stabilizes training by normalizing activations; includes BatchNorm, LayerNorm, GroupNorm |
| Dropout | Randomly deactivates neurons during training to prevent overfitting |
Activations
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| ReLU | max(0, x); fast, widely used in deep networks |
| Sigmoid | S-shaped, output in (0, 1); used in binary classification |
| Tanh | Like sigmoid but centered at 0; output in (-1, 1) |
| Softmax | Outputs a probability distribution; used in final layer of multi-class classification |
Networks
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Feedforward (FFNN) | Basic architecture with no loops; used for static input-output tasks |
| RNN | Handles sequential data using recurrence; remembers previous inputs |
| CNN | Uses convolutions to process grid-like data such as images |
| Transformer | Uses self-attention to model sequences without recurrence; state-of-the-art in NLP & beyond |
Gradient Descent
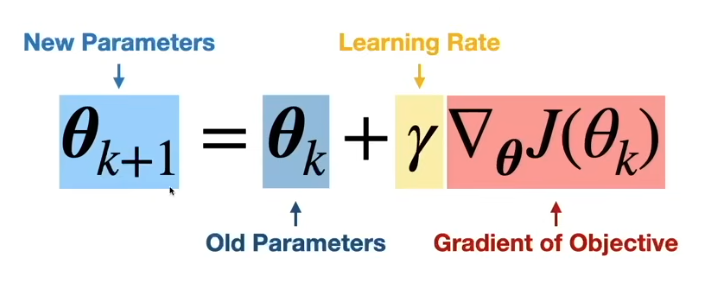
Optimzier
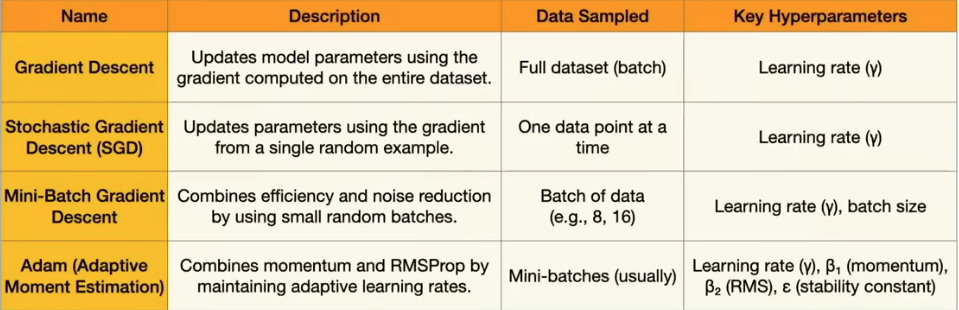
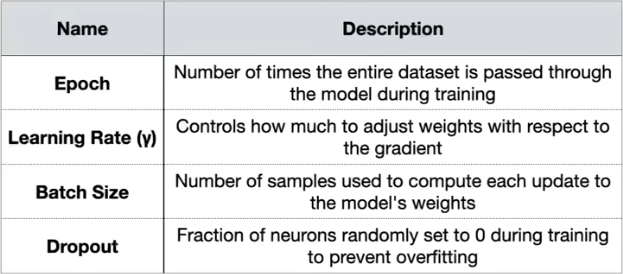
Hyperparameters
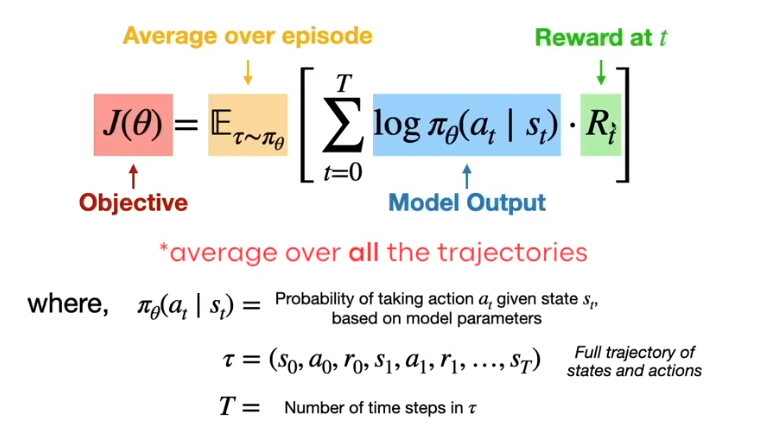
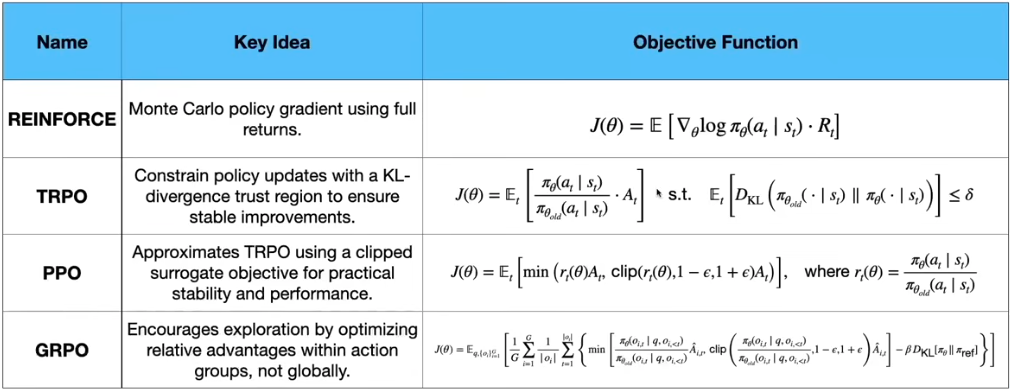
Reinforcement Learning
Dataset
- About Train, Validation and Test Sets in Machine Learning
- What Is Balanced And Imbalanced Dataset?
- How to Build A Data Set For Your Machine Learning Project
- Impact of Dataset Size on Deep Learning Model Skill And Performance Estimates
- Best practices for creating training data
Machine Learning (ML)
- The Future of AI; Bias Amplification & Algorithmic Determinism
- What Do You Need to Know About the Limits of Machine Learning?
- The Limitations of Machine Learning
- The Limitations of Deep Learning
- Ethics of ML
ML on embedded devices
- TinyML models — what happens behind the scenes
- Signal processing is key to embedded Machine Learning
ML pipeline
Feature Selection and Extraction
- Feature Selection and Feature Extraction in Machine Learning: An Overview
- What is the difference between feature extraction and feature selection?
- Average and Root Mean Square (RMS) Calculations
- But what is the Fourier Transform? A visual introduction.
- Why the Power Spectral Density (PSD) Is the Gold Standard of Vibration Analysis
Neural Networks and Training
- Machine Learning for Beginners: An Introduction to Neural Networks
- Youtube: An Introduction to Neural Networks
- how neural networks work with forward- and backpropagation
- Using neural nets to recognize handwritten digits
- A Gentle Introduction to the Rectified Linear Unit (ReLU)
- A Simple Explanation of the Softmax Function
- Keras Layers API
Speech and Language Processing
Model Evaluation, Underfitting, and Overfitting
- Confusion Matrix
- Everything you Should Know about Confusion Matrix for Machine Learning
- Beyond Accuracy: Precision and Recall
- StackExchange: How to calculate precision and recall in a 3 x 3 confusion matrix
- Youtube: Underfitting in a Neural Network
- Youtube: Overfitting and a Neural Network
- Caltech Lecture: Overfitting
- Dropout: A Simple Way to Prevent Neural Networks from Overfitting
Anomaly Detection
- Anomaly Detection for Dummies
- Anomaly Detection with Machine Learning: An Introduction
- Detection in Time-Series Data and K-Means Clustering
- K Means
Convolutional Neural Networks(CNN)
- CNN: A Comprehensive Guide to Convolutional Neural Networks
- Notes about CNNs from Stanford's CS231n course
- Youtube: Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) explained
- Youtube: MIT 6.S191(2020): Convolutional Neural Networks Lecture
- Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN): Step 1(b) - ReLU Layer
- 1D Convolutional Neural Networks and Applications – A Survey
- A Gentle Introduction to Dropout for Regularizing Deep Neural Networks
- How to Configure the Learning Rate When Training Deep Learning Neural Networks
- Fourier Transform
Sample Rate and Bit Depth
- how speakers work
- how to covers the common audio sample rates
- Data Augmentation | How to use Deep Learning when you have Limited Data — Part 2
- Digital Audio Basics: Sample Rate and Bit Depth
Mel Frequency Cepstral Coefficient(MFCC)
- The Nyquist–Shannon Theorem
- Sampling Theorem and Frequency Spectrum Aliasing
- Mel Frequency Cepstral Coefficient (MFCC)
- Speech Processing for Machine Learning: Filter banks, Mel-Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCCs) and What's In-Between
- Sensor Fusion
AI Accelerator
- What Makes a Good AI Accelerator
- How to Make Your Own Deep Learning Accelerator Chip
- DNN Accelerator Architecture - SIMD or Systolic?
Image Classification and Neural Networks
- How Does Image Classification Work?
- Basic classification: Classify images of clothing
- PIL.Image
- scikitimage.transform
- OpenMV
CNN Visualizations and Data Augmentation
- Saliency map
- Grad-CAM: Visualize class activation maps with Keras, TensorFlow, and Deep Learning
- Neural Network Interpretation
- Grad-CAM: Visual Explanations from Deep Networks via Gradient-based Localization
- Data Augmentation - How to Use Deep Learning When You have Limited Data--Part 2
- How to Configure Image Data Augmentation in Keras
- A survey on Image Data Augmentation for Deep Learning
Transfer Learning
- A Gentle Introduction to Transfer Learning for Deep learning
- Transfer learning - Machine Learning's Next Frontier
- Youtube - Transfer Learning
- A Comprehensive Hands-on Guide to Transfer Learning with Real-World Applications in Deep Learning
- An Overview on MobileNet: An Efficient Mobile Vision CNN
- MobileNets: Efficient Convolutional Neural Networks for Mobile Vision Application
Object Detection
- Classification: Precision and Recall
- Intersection over Union (IoU) for Object Detection
- mAP (mean Average Precision) for Object Detection
- The PASCAL Visual Object Classes (VOC) Challenge
- COCO Detection Evaluation Metrics
R-CNN
- Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation (R-CNN)
- Fast R-CNN
- Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks
- SSD: Single Shot MultiBox Detector
- Feature Pyramid Networks for Object Detection
- YOLOv4: Optimal Speed and Accuracy of Object Detection
- Speed/accuracy trade-offs for modern convolutional object detectors
Advanced Image Processing
- Fully Convolutional Networks for Semantic Segmentation
- U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation
- Mask R-CNN
- Faster R-CNN for Robust Pedestrian Detection Using Semantic Segmentation Network
- Optimizing the Trade-off between Single-Stage and Two-Stage Deep Object Detectors using Image Difficulty Prediction
- Self-Supervised Learning Methods for Computer Vision
- Multi-task Self-Supervised Visual Learning
Neural network architecture example
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, InputLayer, Dropout, Conv1D, Conv2D, Flatten, Reshape, MaxPooling1D, MaxPooling2D, AveragePooling2D, BatchNormalization, Permute, ReLU, Softmax
from tensorflow.keras.optimizers.legacy import Adam
EPOCHS = args.epochs or 100
LEARNING_RATE = args.learning_rate or 0.005
# If True, non-deterministic functions (e.g. shuffling batches) are not used.
# This is False by default.
ENSURE_DETERMINISM = args.ensure_determinism
# this controls the batch size, or you can manipulate the tf.data.Dataset objects yourself
BATCH_SIZE = args.batch_size or 32
if not ENSURE_DETERMINISM:
train_dataset = train_dataset.shuffle(buffer_size=BATCH_SIZE*4)
train_dataset=train_dataset.batch(BATCH_SIZE, drop_remainder=False)
validation_dataset = validation_dataset.batch(BATCH_SIZE, drop_remainder=False)
# model architecture
model = Sequential()
model.add(Reshape((int(input_length / 13), 13), input_shape=(input_length, )))
model.add(Conv1D(8, kernel_size=3, padding='same', activation='relu'))
model.add(MaxPooling1D(pool_size=2, strides=2, padding='same'))
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
model.add(Conv1D(16, kernel_size=3, padding='same', activation='relu'))
model.add(MaxPooling1D(pool_size=2, strides=2, padding='same'))
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
model.add(Flatten())
model.add(Dense(classes, name='y_pred', activation='softmax'))
# this controls the learning rate
opt = Adam(learning_rate=LEARNING_RATE, beta_1=0.9, beta_2=0.999)
callbacks.append(BatchLoggerCallback(BATCH_SIZE, train_sample_count, epochs=EPOCHS, ensure_determinism=ENSURE_DETERMINISM))
# train the neural network
model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer=opt, metrics=['accuracy'])
model.fit(train_dataset, epochs=EPOCHS, validation_data=validation_dataset, verbose=2, callbacks=callbacks)
# Use this flag to disable per-channel quantization for a model.
# This can reduce RAM usage for convolutional models, but may have
# an impact on accuracy.
disable_per_channel_quantization = False
Page Source